 1
1  1
1  1
1 Option A : the fern transitined from gametophyte generation to sporophyte generation.

for six years an artificial fertilizer is used on a apple orchard the orchard is next to a stream which empties in to a slat water bay during the last 5 years researchers have observed an increase in algae in the bay they have also sampled fish populations in the bay each year apex...



A spring is a natural discharge point of subterranean water at the surface of the ground or directly into the bed of a stream, lake, or sea. Water that emerges at the surface without a perceptible current is called a seep. Wells are holes excavated to bring water and other underground fluids to the surface.

The image shows a cross-section of land scape.

Need this store of protein:
The seed consists of three components: embryo, endosperm (sometimes perisperm), and seed-coat. Both endosperm and embryo are the products of double fertilization, whereas the seed-coat develops from the maternal, ovular tissues. The seed habit is a significant advancement in the evolution of higher plants.
Anatomy of seed :-
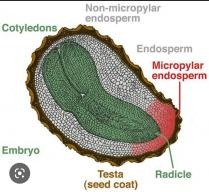

Seed storage proteins provide a source of amino acids and reduced N necessary for germination and early growth of the seedling.
The T-chart by categorizing each statement as something that would most likely be relevant to gene flow or genetic drift. Some answers will fit in both columns depending on the situation. is random is a mechanism for evolution is often related to disasters is also called “migration” deals with movement between populations...


Consumers are dissatisfied with the way that large corporate farms are treating nature's natural resources.


It will provide an instant answer!
