 5
5 The velocity of the vehicle at 0 s is 0 m/s
Explanation:
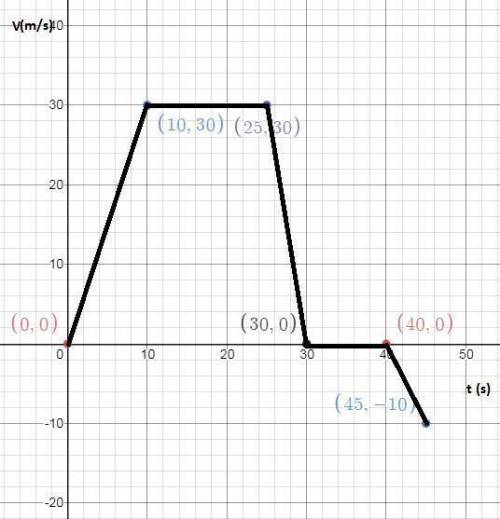
The Velocity vs. Time graph of this situation is shown in the attached image. As we can see, we have five segments:
1) When the vehicle accelerates from 0 to 30 m/s in 10 seconds, which means at 0 seconds the vehicle's velocity was 0 m/s. In addition, as the vehicle goes from zero to a positive velocity, we have a positive slope.
2) Then the vehicle travels for 15 seconds at a constant velocity, that is why we do not have a slope in this section, since the vehicle kept its 30 m/s.
3) The vehicle comes to a stop in the next 5 seconds, that is why we observe an abrupt change in the graph and a negative slope.
4) The car waits 10 seconds in that stop, again we have a line with no slope
5) Finally, the car accelerates from 0 to -10 m/s in the next 5 seconds. This means the car changed its direction.
 40
40 The velocity of the vechicle at 0 s is 0 m/s
Explanation:
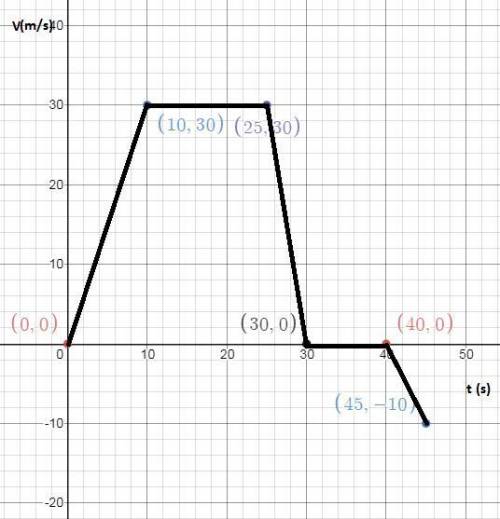
The Velocity vs. Time graph of this situation is shown in the attached image. As we can see, we have five segments:
1) When the vehicle accelerates from 0 to 30 m/s in 10 seconds, which means at 0 seconds the vehicle's velocity was 0 m/s. In addition, as the vehicle goes from zero to a positive velocity, we have a positive slope.
2) Then the vehicle travels for 15 seconds at a constant velocity, that is why we do not have a slope in this section, since the vehicle kept its 30 m/s.
3) The vehicle comes to a stop in the next 5 seconds, that is why we observe an abrupt change in the graph and a negative slope.
4) The car waits 10 seconds in that stop, again we have a line with no slope
5) Finally, the car accelerates from 0 to -10 m/s in the next 5 seconds. This means the car changed its direction.
 5
5 The velocity of the vehicle at 0 s is 0 m/s
Explanation:
The Velocity vs. Time graph of this situation is shown in the attached image. As we can see, we have five segments:
1) When the vehicle accelerates from 0 to 30 m/s in 10 seconds, which means at 0 seconds the vehicle's velocity was 0 m/s. In addition, as the vehicle goes from zero to a positive velocity, we have a positive slope.
2) Then the vehicle travels for 15 seconds at a constant velocity, that is why we do not have a slope in this section, since the vehicle kept its 30 m/s.
3) The vehicle comes to a stop in the next 5 seconds, that is why we observe an abrupt change in the graph and a negative slope.
4) The car waits 10 seconds in that stop, again we have a line with no slope
5) Finally, the car accelerates from 0 to -10 m/s in the next 5 seconds. This means the car changed its direction.

 40
40 The velocity of the vechicle at 0 s is 0 m/s
Explanation:
The Velocity vs. Time graph of this situation is shown in the attached image. As we can see, we have five segments:
1) When the vehicle accelerates from 0 to 30 m/s in 10 seconds, which means at 0 seconds the vehicle's velocity was 0 m/s. In addition, as the vehicle goes from zero to a positive velocity, we have a positive slope.
2) Then the vehicle travels for 15 seconds at a constant velocity, that is why we do not have a slope in this section, since the vehicle kept its 30 m/s.
3) The vehicle comes to a stop in the next 5 seconds, that is why we observe an abrupt change in the graph and a negative slope.
4) The car waits 10 seconds in that stop, again we have a line with no slope
5) Finally, the car accelerates from 0 to -10 m/s in the next 5 seconds. This means the car changed its direction.

 1
1 5. 6319 N
First of all, we need to find the acceleration of the car, which can be found by using the equation
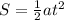
where
S = 40.0 m is the distance travelled by the car
t = 3.0 s is the time taken
a is the acceleration
Solving for a, we find
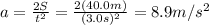
So now since we know the mass of the car, m=710 kg, we can find the net force acting on the car:
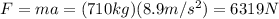
6. 62.5 m
In this case, we know the breaking force applied on the car,
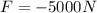
(with a negative sign since its direction is opposite to the car's motion)
and the mass of the car
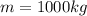
so we can find its acceleration:
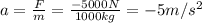
So now we can find the minimum distance to stop by using the equation
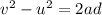
where in this case we have
v = 0 m/s is the final speed
u = 25 m/s is the initial speed
a = -5 m/s^2 is the acceleration
d is the distance
solving for d,
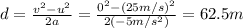
7a. 14 m/s
We can solve the problem by using the law of conservation of energy: in fact, the initial gravitational potential energy of the person is all converted into kinetic energy as she hits the water below
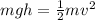
where
m = 65 kg is the mass of the person
g = 9.8 m/s^2
h = 10 m is the initial height of the diver
v is the final speed as she enters the water
Solving for v, we find
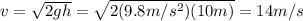
7b. -3185 N
We need to find the acceleration of the diver during the motion of 2.0 m below the water:
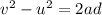
where
v = 0 is the final speed
u = 14 m/s is the initial speed as she enters the water
a is the acceleration
d = 2.0 m is the distance covered
Solving for a,
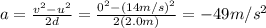
And so now we can find the net force acting on the diver
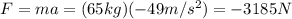
8a. -133 m/s^2
The acceleration of the passenger is given by
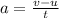
where
v = 0 m/s is the final speed
u = 13.3 m/s is the initial speed
t = 0.10 s is the time interval
Solving for a, we find
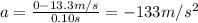
8b. 3325 N
The force that the driver must exert on the child is equal in magnitude to the force experienced by the child during the stop of the car, so
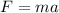
where
m = 25 kg is the mass of the child
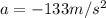 is the acceleration
is the acceleration
So, the magnitude of the force will be
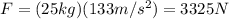
8c. 245 N
The weight of the child is given by
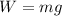
where
m = 25 kg is the child's mass
g = 9.8 m/s^2 is the acceleration due to gravity
Solving the equation,
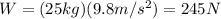
8d. 55.1 lb
Since we know that
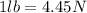
We can find the weight in pounds by setting the following proportion
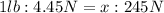
Solving for x,
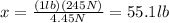
8e. Chances are very low
The force that the driver should exert on the child is
F = 3325 N
This force is equivalent to the force required to lift an object of mass m:
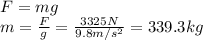
So, it is equivalent to the force required to lift an object of 339.3 kg, which is quite a lot. therefore, the changes are very low.
 12
12 19. D. A car moving northeast at 90 km/hr
To answer this question you have to know the difference between velocity and speed. Velocity is the same as speed, but with direction. Option A and option B doesn't even have speed as it don't give a distance per time unit. Option C have speed, but doesn't have direction so it doesn't have velocity.
20. C. Accel 1 has a constant rate of acceleration; Accel 2 accelerates at different rates during the trip.
The velocity graph of Accel 1 is an upward straight line. This show that the velocity keep increasing through the entire trip, so it should have constant positive acceleration the entire trip.
The velocity graph of Accel 2 start with higher upward straight line, but then downward until zero. This show there is a positive acceleration on the first trip, but then become negative at the end. There is a change in the Accel 2 acceleration.
21. C) 200 N right
From the picture, the object has 50N downward force, 50N upward force and 200N force to the right.
The sum of the force in vertical direction would be: 50N- 50N=0N.
The sum of the force in horizontal direction would be: 200N.
The answer will be 200N to the right
22. d) a toy car moving east at a constant velocity
When the net force of an object is greater than zero, the force will be converted into kinetic energy which will increase the velocity the object. This will allow the object to have acceleration. A glass resting and a ladder leaning against a wall doesn't even have velocity. A toy car moving east at a constant velocity, doesn't have acceleration.
23. B. increases.
Gravity cause the object to have potential energy. Gravity force is directly related to the mass and inversely related to the distance square of the object. If the mass increases, then potential energy of the object would be increased too.
24. C. The part will move at a constant speed along a straight path until it is acted upon by another force.
The part get energy from the astronaut force which converted into kinetic energy. As long as the part having kinetic energy, it will continually move. Since the space has no air, there will be no air to stop the part. The part will continue to move at constant speed(no acceleration) until any force bump into it.
25. D. The hockey stick will change the speed of the puck and make it accelerate.
If an object collide with another stationary object, some of the kinetic energy will be transferred. The kinetic energy of the hockey stick will be transferred to the puck, which cause the puck to have acceleration. The hockey stick will lose some energy and become a bit slower because of this.
26. D. For every action your cat makes, there is an equal and opposite reaction from the string.
This case is similar to the previous question. When the cat moving her paw and collide with the toy(action), there will be some force put on both the toy and cat paw. The force will cause the toy accelerate and make it moving away from the cat(reaction) while reducing the kinetic energy of the cat paw.
27 B. They hit each other with the same force in opposite directions.
This will also be explained by Newton's third law of motion. For every action there will be equal opposite reaction. When baseball and bat collide, the action from baseball will cause reaction on the bat and the baseball. The action from the bat also will cause reaction on the bat and the baseball too.
 1
1 5. 6319 N
First of all, we need to find the acceleration of the car, which can be found by using the equation
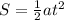
where
S = 40.0 m is the distance travelled by the car
t = 3.0 s is the time taken
a is the acceleration
Solving for a, we find
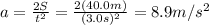
So now since we know the mass of the car, m=710 kg, we can find the net force acting on the car:
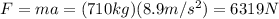
6. 62.5 m
In this case, we know the breaking force applied on the car,
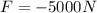
(with a negative sign since its direction is opposite to the car's motion)
and the mass of the car
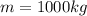
so we can find its acceleration:
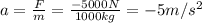
So now we can find the minimum distance to stop by using the equation
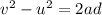
where in this case we have
v = 0 m/s is the final speed
u = 25 m/s is the initial speed
a = -5 m/s^2 is the acceleration
d is the distance
solving for d,
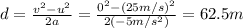
7a. 14 m/s
We can solve the problem by using the law of conservation of energy: in fact, the initial gravitational potential energy of the person is all converted into kinetic energy as she hits the water below
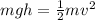
where
m = 65 kg is the mass of the person
g = 9.8 m/s^2
h = 10 m is the initial height of the diver
v is the final speed as she enters the water
Solving for v, we find
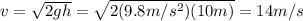
7b. -3185 N
We need to find the acceleration of the diver during the motion of 2.0 m below the water:
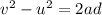
where
v = 0 is the final speed
u = 14 m/s is the initial speed as she enters the water
a is the acceleration
d = 2.0 m is the distance covered
Solving for a,
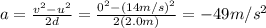
And so now we can find the net force acting on the diver
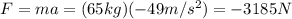
8a. -133 m/s^2
The acceleration of the passenger is given by
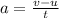
where
v = 0 m/s is the final speed
u = 13.3 m/s is the initial speed
t = 0.10 s is the time interval
Solving for a, we find
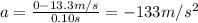
8b. 3325 N
The force that the driver must exert on the child is equal in magnitude to the force experienced by the child during the stop of the car, so
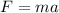
where
m = 25 kg is the mass of the child
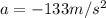 is the acceleration
is the acceleration
So, the magnitude of the force will be
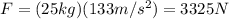
8c. 245 N
The weight of the child is given by
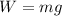
where
m = 25 kg is the child's mass
g = 9.8 m/s^2 is the acceleration due to gravity
Solving the equation,
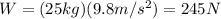
8d. 55.1 lb
Since we know that
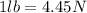
We can find the weight in pounds by setting the following proportion
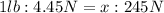
Solving for x,
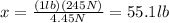
8e. Chances are very low
The force that the driver should exert on the child is
F = 3325 N
This force is equivalent to the force required to lift an object of mass m:
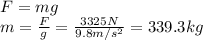
So, it is equivalent to the force required to lift an object of 339.3 kg, which is quite a lot. therefore, the changes are very low.
 12
12 19. D. A car moving northeast at 90 km/hr
To answer this question you have to know the difference between velocity and speed. Velocity is the same as speed, but with direction. Option A and option B doesn't even have speed as it don't give a distance per time unit. Option C have speed, but doesn't have direction so it doesn't have velocity.
20. C. Accel 1 has a constant rate of acceleration; Accel 2 accelerates at different rates during the trip.
The velocity graph of Accel 1 is an upward straight line. This show that the velocity keep increasing through the entire trip, so it should have constant positive acceleration the entire trip.
The velocity graph of Accel 2 start with higher upward straight line, but then downward until zero. This show there is a positive acceleration on the first trip, but then become negative at the end. There is a change in the Accel 2 acceleration.
21. C) 200 N right
From the picture, the object has 50N downward force, 50N upward force and 200N force to the right.
The sum of the force in vertical direction would be: 50N- 50N=0N.
The sum of the force in horizontal direction would be: 200N.
The answer will be 200N to the right
22. d) a toy car moving east at a constant velocity
When the net force of an object is greater than zero, the force will be converted into kinetic energy which will increase the velocity the object. This will allow the object to have acceleration. A glass resting and a ladder leaning against a wall doesn't even have velocity. A toy car moving east at a constant velocity, doesn't have acceleration.
23. B. increases.
Gravity cause the object to have potential energy. Gravity force is directly related to the mass and inversely related to the distance square of the object. If the mass increases, then potential energy of the object would be increased too.
24. C. The part will move at a constant speed along a straight path until it is acted upon by another force.
The part get energy from the astronaut force which converted into kinetic energy. As long as the part having kinetic energy, it will continually move. Since the space has no air, there will be no air to stop the part. The part will continue to move at constant speed(no acceleration) until any force bump into it.
25. D. The hockey stick will change the speed of the puck and make it accelerate.
If an object collide with another stationary object, some of the kinetic energy will be transferred. The kinetic energy of the hockey stick will be transferred to the puck, which cause the puck to have acceleration. The hockey stick will lose some energy and become a bit slower because of this.
26. D. For every action your cat makes, there is an equal and opposite reaction from the string.
This case is similar to the previous question. When the cat moving her paw and collide with the toy(action), there will be some force put on both the toy and cat paw. The force will cause the toy accelerate and make it moving away from the cat(reaction) while reducing the kinetic energy of the cat paw.
27 B. They hit each other with the same force in opposite directions.
This will also be explained by Newton's third law of motion. For every action there will be equal opposite reaction. When baseball and bat collide, the action from baseball will cause reaction on the bat and the baseball. The action from the bat also will cause reaction on the bat and the baseball too.
 1
1 -6
Explanation:
a=vf-vi/t
vf=0
so that we you subtract vf to vi it will be -30/5=-6
 112
112 
It will provide an instant answer!
