 3
3 158.76 cm²
Step-by-step explanation:
Quadrilateral ABCD is composed of 2 right triangles
Construct the line BD, then
Δ ABD and Δ BCD are the 2 right triangles.
The area (A) of a triangle is calculated using
A = 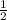 bh ( b is the base and h the perpendicular height )
bh ( b is the base and h the perpendicular height )
Δ ABD with b = 18 and h = 7.5
A = 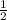 × 18 × 7.5 = 9 × 7.5 = 67.5 cm²
× 18 × 7.5 = 9 × 7.5 = 67.5 cm²
Δ BCD with b = 15.6 and h = 11.7
A = 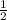 × 15.6 × 11.7 = 7.8 × 11.7 = 91.26 cm²
× 15.6 × 11.7 = 7.8 × 11.7 = 91.26 cm²
Thus
area of ABCD = 67.5 + 91.26 = 158.76 cm²
 3
3 158.76 cm²
Step-by-step explanation:
Quadrilateral ABCD is composed of 2 right triangles
Construct the line BD, then
Δ ABD and Δ BCD are the 2 right triangles.
The area (A) of a triangle is calculated using
A = 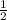 bh ( b is the base and h the perpendicular height )
bh ( b is the base and h the perpendicular height )
Δ ABD with b = 18 and h = 7.5
A = 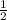 × 18 × 7.5 = 9 × 7.5 = 67.5 cm²
× 18 × 7.5 = 9 × 7.5 = 67.5 cm²
Δ BCD with b = 15.6 and h = 11.7
A = 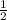 × 15.6 × 11.7 = 7.8 × 11.7 = 91.26 cm²
× 15.6 × 11.7 = 7.8 × 11.7 = 91.26 cm²
Thus
area of ABCD = 67.5 + 91.26 = 158.76 cm²
 1
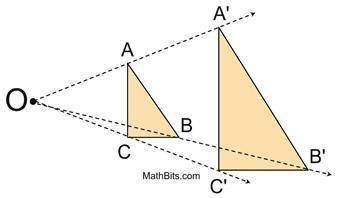
1 D) Quadrilateral ABCD and quadrilateral A'B'C'D' have the same angle measures.
Step-by-step explanation:
A dilation basically just means that the shape gets proportionately larger (see attached file).
A cannot be true because of the dilation. The shape is now larger than it was by a factor of eight. Therefore the area will not be the same.
B and C are also not true for basically the same reasons. Shape is bigger, therefore the length of the sides are longer and the perimeter is larger.
The only thing that is not affected by a dilation are the shapes angle measures. If those were affected, A'B'C'D' would not be a dilation of ABCD.
Hope this helps.
 1
1 D) Quadrilateral ABCD and quadrilateral A'B'C'D' have the same angle measures.
Step-by-step explanation:
A dilation basically just means that the shape gets proportionately larger (see attached file).
A cannot be true because of the dilation. The shape is now larger than it was by a factor of eight. Therefore the area will not be the same.
B and C are also not true for basically the same reasons. Shape is bigger, therefore the length of the sides are longer and the perimeter is larger.
The only thing that is not affected by a dilation are the shapes angle measures. If those were affected, A'B'C'D' would not be a dilation of ABCD.
Hope this helps.

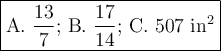
Step-by-step explanation:
A. Scale factor
When you dilate an object by a scale factor, you multiply its line lengths by the same number.
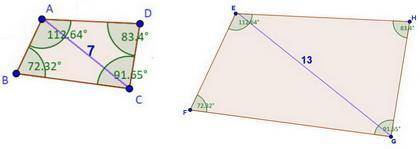
If EF/AB = 13/7, the scale factor is 13/7.
B. Length of EF
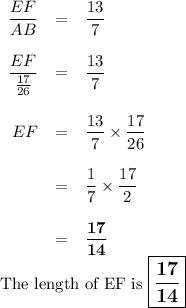
C. Area of EFGH
If the lengths in a shape are all multiplied by a scale factor, then the areas will be multiplied by the scale factor squared.
ABCD is dilated by a scale factor of 13/7, so its area is dilated by a scale factor of
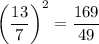
The area of its dilated image EFGH is
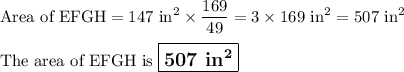
 2
2 13/7, 221/182 and expansion, 507 inches
Step-by-step explanation:
If the two quadrilaterals are similar, you can take the diagonal length as a similar side to find the scale factor. In this case, the scale factor would be 13/7. For simplicity, we can keep this a factor for now. Because the quadrilaterals are similar, the scale factor is the same for all sides, 13/7. Because you are going from ABCD to EFGH and the scale factor is 13/7 (otherwise the other way around would be 7/13) and so the scale factor is greater than 1, you are expanding aka expansion. So, to find EF from side AB and you have the length 17/26, just multiply that by 13/7 to get 221/182 as the length.
To find the area of EFGH, you square the scale factor 13/7 and equal it to the area of EFGH A is over the area of the ABCD (you ratio them and set them equal) so 169/49 = A/147 and solve for A which is then 49A = 169 x 147 which is then 507 inches.
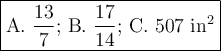
Step-by-step explanation:
A. Scale factor
When you dilate an object by a scale factor, you multiply its line lengths by the same number.
If EF/AB = 13/7, the scale factor is 13/7.
B. Length of EF
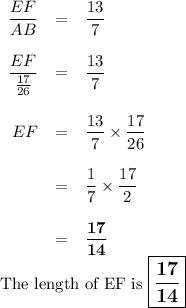
C. Area of EFGH
If the lengths in a shape are all multiplied by a scale factor, then the areas will be multiplied by the scale factor squared.
ABCD is dilated by a scale factor of 13/7, so its area is dilated by a scale factor of
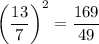
The area of its dilated image EFGH is
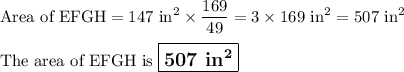

 1
1 The question is incomplete. Here is the complete question.
Quadrilateral EFGH is a scaled copy of quadrilateral ABCD. Select all of the true statements.
A. Segment EF is twice as long as segment AB.
B. Segment CD is twice as long as segment FG
C. The measure of angle HEF is twice the measure of angle DAB
D. The length of segment EH is 16 units.
E. The area of EFGH is twice the area of ABCD.
A. Segment EF is twice as long as segment AB
D. The length of segment EH is 16 units
E. The area of EFGH is twice the area of ABCD
Step-by-step explanation: One quadrilateral which is scaled copy of another quadrilateral means both quadrilateral are similar, i.e., they have congruent angles (same angles) but different sides lengths.
Comparing side GH with side CD, you notice GH's length is twice the side CD. This relationship between each corresponding sides is called scale factor.
Analysing statements above:
A. This statement is correct because segments EF and AB are corresponding sides, so EF will be twice as much as AB;
B. This is incorrect because they are not corresponding sides, so they are not related;
C. Is incorrect because measure of angle in similar quadrilateral has the exact same angle;
D. Statement is correct because if segment AD is 8 units, the corresponding segment EH will be:
EH = 2 x 8 = 16 units
E. Tis statement is correct because area of quadrilateral ABCD is proportional to the area of quadrilateral EFGH by the scale factor, therefore, area of EFGH is twice the area of ABCD.
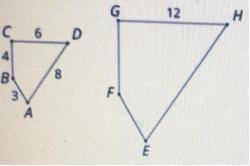
 11
11 ✔️Segment EF is twice as long as segment AB
✔️The length of segment EH is 16 units.
Step-by-step explanation:
Since quadrilateral ABCD is scaled to form quadrilateral EFGH, both are similar polygon.
Therefore: scale factor = ratio of any of their corresponding side
Scale factor = GH/CD = 12/6 = 2
This means quadrilateral EFGH is twice the size of quadrilateral ABCD.
The shape of the original polygon remains the same while the size increases.
This implies that, all segments of quadrilateral ABCD increases proportionally times 2 to give us corresponding lengths of the segments of quadrilateral EFGH.
Since shape remains the same, their corresponding angles are congruent and the same in measure.
Therefore, the following statements are true and correct:
✔️Segment EF is twice as long as segment AB
(EF = AB*scale factor = 3*2 = 6)
✔️The length of segment EH is 16 units.
(EH = AD*scale factor = 8*2 = 16)
 23
23 A and D
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that EFGH is a scaled copy of ABCD, EFGH is similar to ABCD. The ratio of the corresponding lenght of their segments are equal, and therefore have the same scale factor.
This means: 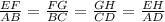
We are given only the length of segment GH = 12. GH corresponds with segment CD = 6, therefore:
Scale factor = 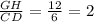 .
.
This implies that all length segments of ABCD was increased by 2 to get a scale copy of EFGH.
Angles in EFGH will have the same measures of degree as the corresponding angles in ABCD, because, it would have the same shape but only different in size.
The following statements are therefore true:
A. Segment EF is twice as long as segment AB. (Scale factor = 2)
D. The length of segment EH is 16 units. (EH = 2*AD = 2*8 = 16)

It will provide an instant answer!
