 6
6 Part 1 : Equation: ( 3x - 9 ) + 30 + 24 = 180,
Part 2 : Value of x ⇒ 45°,
Part 3 : Measure of Angle U ⇒ 126°
Step-by-step explanation:
~ Part 1 ~
We know that ∑ of angles in a triangle is 180;
m∠ U + m∠ V + m∠ W = 180°,
Equation: ( 3x - 9 ) + 30 + 24 = 180
~ Part 2 ~
Now let us simplify the equation above to solve for x;
3x - 9 + 30 + 24 = 180,
3x - 9 = 126,
3x = 135,
x = 45 degrees ( ° ) ⇒
Value of x ⇒ 45°
~ Part 3 ~
If it is known that m∠ U ⇒ 3x - 9;
m∠ U = 3 * ( 45 ) - 9,
m∠ U = 135 - 9,
m∠ U = 126 degrees ( ° ) ⇒
Measure of Angle U ⇒ 126°
 6
6 Part 1 : Equation: ( 3x - 9 ) + 30 + 24 = 180,
Part 2 : Value of x ⇒ 45°,
Part 3 : Measure of Angle U ⇒ 126°
Step-by-step explanation:
~ Part 1 ~
We know that ∑ of angles in a triangle is 180;
m∠ U + m∠ V + m∠ W = 180°,
Equation: ( 3x - 9 ) + 30 + 24 = 180
~ Part 2 ~
Now let us simplify the equation above to solve for x;
3x - 9 + 30 + 24 = 180,
3x - 9 = 126,
3x = 135,
x = 45 degrees ( ° ) ⇒
Value of x ⇒ 45°
~ Part 3 ~
If it is known that m∠ U ⇒ 3x - 9;
m∠ U = 3 * ( 45 ) - 9,
m∠ U = 135 - 9,
m∠ U = 126 degrees ( ° ) ⇒
Measure of Angle U ⇒ 126°
 178
178 The measure of an angle, that forms a known larger angle with another
known angle can be determined by angle addition postulate.
Correct responses:
1. a) Point B
b) 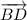 and
and 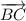
c) ∠EBD
d) ∠FBC = Right angle
e) ∠EBF = An obtuse angle
f) ∠ABC = Straight angle
g) 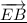
h) m∠EBC = 180°
i) 36°
2) x = 6°
3) x = 4°
Methods by which the above values are obtaineda) The vertex of an angle is the point where the lines forming the angles meet.
The vertex of the angle ∠4 = Point Bb) The sides of an angle are the rays that form the angle.
The sides of ∠1 =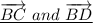
c) The name of an angle can be given by the three points of the angle
Therefore;
Another name of angle ∠5 is ∠EBDd) Given that 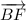 ⊥
⊥ 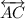 , we have;
, we have;
e) ∠EBF = An obtuse angle
f) ∠ABC = 180° = Straight angle
g) Given that by symbol for equal angles in the diagram, we have;
∠EBD = ∠ABE
Therefore, segment 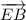 bisects ∠ABD
bisects ∠ABD
Which gives;
An angle bisector is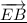
h) m∠EBD = 36°, m∠DBC = 108°
m∠EBC = m∠ABE + m∠EBD + m∠DBC (angle addition property)
m∠EBC = m∠EBD + m∠EBD + m∠DBC (substitution property)
Therefore;
m∠EBC = 36° + 36° + 108° = 180°i) m∠EBF = 117°
m∠EBF = m∠ABE + m∠ABF
m∠ABF = m∠FBC = 90°
Therefore;
117° = m∠ABE + 90°
m∠ABE = 117° - 90° = 27°2. Given:
m∠MKL = 83°, m∠JKL = 127°, m∠JKM = (9·x - 10)°
Required:
The value of x
Solution:
m∠JKL = m∠MKL + m∠JKM
Which by plugging in the values gives;
127° = 83° + (9·x - 10)°
127° - 83° = 44° = (9·x - 10)°
44° + 10° = 54° = 9·x
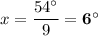
3. m∠EFH = (5·x + 1)°
m∠HFG = 62°
m∠EFG = (18·x + 11)°
By angle addition property, we have;
m∠EFG = m∠EFH + m∠HFG
Therefore;
18·x + 11 = 5·x + 1 + 62
18·x - 5·x = 62 + 1 - 11 = 52
13·x = 52
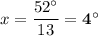
Learn more about angle addition property here:
link
 178
178 The measure of an angle, that forms a known larger angle with another
known angle can be determined by angle addition postulate.
Correct responses:
1. a) Point B
b) 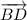 and
and 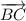
c) ∠EBD
d) ∠FBC = Right angle
e) ∠EBF = An obtuse angle
f) ∠ABC = Straight angle
g) 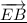
h) m∠EBC = 180°
i) 36°
2) x = 6°
3) x = 4°
Methods by which the above values are obtaineda) The vertex of an angle is the point where the lines forming the angles meet.
The vertex of the angle ∠4 = Point Bb) The sides of an angle are the rays that form the angle.
The sides of ∠1 =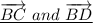
c) The name of an angle can be given by the three points of the angle
Therefore;
Another name of angle ∠5 is ∠EBDd) Given that 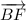 ⊥
⊥ 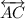 , we have;
, we have;
e) ∠EBF = An obtuse angle
f) ∠ABC = 180° = Straight angle
g) Given that by symbol for equal angles in the diagram, we have;
∠EBD = ∠ABE
Therefore, segment 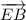 bisects ∠ABD
bisects ∠ABD
Which gives;
An angle bisector is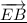
h) m∠EBD = 36°, m∠DBC = 108°
m∠EBC = m∠ABE + m∠EBD + m∠DBC (angle addition property)
m∠EBC = m∠EBD + m∠EBD + m∠DBC (substitution property)
Therefore;
m∠EBC = 36° + 36° + 108° = 180°i) m∠EBF = 117°
m∠EBF = m∠ABE + m∠ABF
m∠ABF = m∠FBC = 90°
Therefore;
117° = m∠ABE + 90°
m∠ABE = 117° - 90° = 27°2. Given:
m∠MKL = 83°, m∠JKL = 127°, m∠JKM = (9·x - 10)°
Required:
The value of x
Solution:
m∠JKL = m∠MKL + m∠JKM
Which by plugging in the values gives;
127° = 83° + (9·x - 10)°
127° - 83° = 44° = (9·x - 10)°
44° + 10° = 54° = 9·x
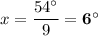
3. m∠EFH = (5·x + 1)°
m∠HFG = 62°
m∠EFG = (18·x + 11)°
By angle addition property, we have;
m∠EFG = m∠EFH + m∠HFG
Therefore;
18·x + 11 = 5·x + 1 + 62
18·x - 5·x = 62 + 1 - 11 = 52
13·x = 52
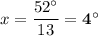
Learn more about angle addition property here:
link
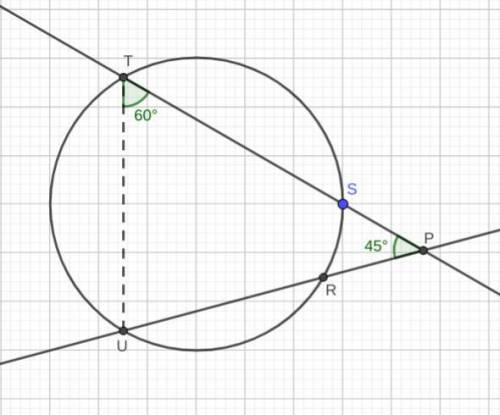
 7
7 Step-by-step explanation:
(a) If RS = x, then the sum of arcs around the circle is ...
x + 4x +4x +3x = 360°
12x = 360°
x = 30°
__
(b) Based on the given ratios, the arc measures are computed from x. For example, ST = TU = 4x = 4(30°) = 120°
RS = 30°ST = 120°TU = 120°UR = 90°__
(c) Angle P is half the difference of arcs TU and RS:
∠P = (TU -RS)/2 = (120° -30°)/2
∠P = 45°
__
(d) Inscribed angle UTS is half the measure of the arc it intercepts. Arc RU has the measure (30° +90°) = 120°, so the measure of UTS is ...
∠UTS = 120°/2 = 60°
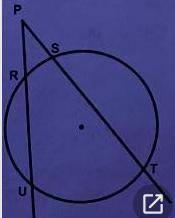
 3
3 (a) x = 30°
(b) mRS = 30°
mST = 120°
mTU = 120°
mUR = 90°
Step-by-step explanation:
In the picture attached, the diagram is shown.
(a) Given that m arc RS = x, from the ratios:
m arc ST = 4x
m arc TU = 4x
m arc UR = 3x
The addition of the four arcs must be equal to 360°, then:
x + 4x + 4x + 3x = 360°
12x = 360°
x = 360°/12 = 30°
(b) m arc RS = x = 30°
m arc ST = 4x = 4*30° = 120°
m arc TU = 4x = 4*30° = 120°
m arc UR = 3x = 3*30° = 90°
mRS = 30°
, mST = 120°
, mTU = 120°
, mUR = 90°
 3
3 (a) x = 30°
(b) mRS = 30°
mST = 120°
mTU = 120°
mUR = 90°
Step-by-step explanation:
In the picture attached, the diagram is shown.
(a) Given that m arc RS = x, from the ratios:
m arc ST = 4x
m arc TU = 4x
m arc UR = 3x
The addition of the four arcs must be equal to 360°, then:
x + 4x + 4x + 3x = 360°
12x = 360°
x = 360°/12 = 30°
(b) m arc RS = x = 30°
m arc ST = 4x = 4*30° = 120°
m arc TU = 4x = 4*30° = 120°
m arc UR = 3x = 3*30° = 90°
mRS = 30°
, mST = 120°
, mTU = 120°
, mUR = 90°

 1
1  1
1  12
12 
It will provide an instant answer!
