Question set:
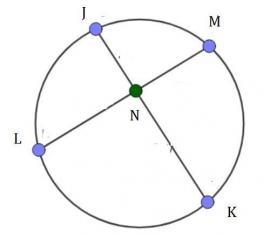
Question 6 For circle H, JN = x, NK = 2, LN = 3, and NM = 6. Solve for x. circle H with chords JK and LM intersecting at N inside the circle 1 7 9 4
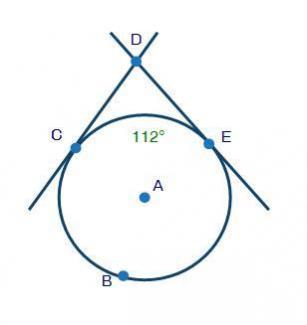
Question 7(Multiple Choice Worth 1 points) (07.01 MC) Lines CD and DE are tangent to circle A: Lines CD and DE are tangent to circle A and intersect at point D. Arc CE measures 112 degrees. Point B lies on circle A. If arc CE is 112°, what is the measure of ∠CDE? 124° 136° 68° 56°
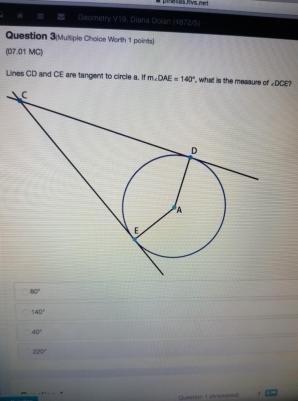
Question 8(Multiple Choice Worth 1 points) (07.01 MC) Lines CD and CE are tangent to circle a. If m∠DAE = 140°, what is the measure of ∠DCE? Tangent CD intersects with circle A at point D, tangent CE intersects with circle A at point E, angle ECD is on the exterior of circle A, and angle DAE has a vertex on the center of circle A. 80° 140° 40° 220°
Question 9(Multiple Choice Worth 1 points) (07.01 MC) Find the measure of arc EC. Circle A with chords EF and CD that intersect at point G, the measure of arc EC is 5x degrees, the measure of angle EGC is 7x degrees, and the measure of arc DF is 90 degrees. 50° 70° 100° 140°
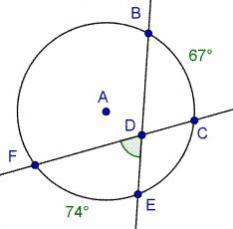
Question 10(Multiple Choice Worth 1 points) (07.01 MC) In circle A, marc BC is 67° and marc EF is 74°: Points B, C, E, and F lie on Circle A. Lines BE and CF pass through point D, creating angle EDF. The measure of arc BC is 67 degrees, and the measure of arc EF is 74 degrees. What is m∠FDE? 37° 74° 70.5° 33.5°
Answer set:
Q. 6
Options:
a. 1
b. 7
c. 9
d. 4
Answer:
c. 9
Step-by-step explanation:
see the attached figure to better understand the problem
we know that
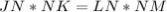 ----> by intersecting chords theorem
----> by intersecting chords theorem
substitute the given values
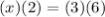
solve for x
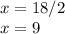
Q. 7
Options:
a 124°
b 136°
c 68°
d 56°
Answer:
c 68°
Explanation:
The measure of ∠CDE is 68degrees
This question bothers on circle geometry;
From the diagram, we can see that ACDE will form a quadrilateral. Since the sum of angles of a quadrilateral is 360degrees, hence;

From the diagram, since CD and DE are both tangential to the circle at point C and E, this shows that <E = <E = 90°
substituting the given values in the formula;
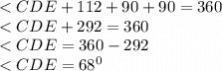
Hence the measure of ∠CDE is 68 degrees
Q. 8
Options:
A - 80°
B - 140°
C - 40°
D - 220°
Answer:
C - 40°
Step-by-step explanation:
From the figure we can see a circle.
CD and CE are the two tangents from a common external point C.
CD = CE
To find the measure of <DCE
Consider the quadrilateral <DAE.
<D = <E = 90° [ Angles made with tangent and radius]
m<DCE + m<DAE = 180°
m<DCE = 180- m<DAE
= 180 - 140
= 40°
The correct answer is option C - 40°
Q. 9
Options:
a. 50°
b. 70°
c. 100°
d. 140°
Answer:
b. 70°
Explanation:
m∠EGC=70°
Step-by-step explanation:
we know that
The measure of the inner angle is the semi-sum of the arcs comprising it and its opposite
so
m∠EGC=(1/2)[arc EC+arc DF]
Find the value of x
we have
m∠EGC=(7x+7)°
arc EC=50°
arc DF=10x°
substitute and solve for x
(7x+7)°=(1/2)[50°+10x°]
14x+14=50+10x
14x-10x=50-14
4x=36
x=9
Find the measure of angle EGC
m∠EGC=(7x+7)°
substitute the value of x
m∠EGC=(7(9)+7)°=70°
Q. 10
Options:
a. 37°
b. 74°
c. 70.5°
d. 33.5°
Answer:
c. 70.5°
Explanation:
So here is how we find the measurement of m∡FDE. Given that mArc BC is 67° and mArc EF is 74°.
<fde=1/2∗(67+74)
<fde = 1/2*(141)
<fde = 70.5
Therefore, the measurement of m∡FDE is 70.5° and that would be the third option. Hope this is the answer that you are looking for.
 99
99 The relationship between the angles formed in a circle are described by
circle theorems.
The true statements are;
m∠EFD ≅ m∠EGD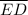 ≅
≅ 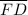
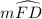 = 120°
= 120°Reasons:
According to the outside angle theorem, we have;
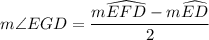
Therefore;
2 × m∠EGD = 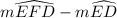
2 × 60° = 120° = 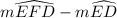
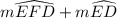 = 360° sum of angles formed at the center of the circle
= 360° sum of angles formed at the center of the circle
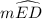 = 360° -
= 360° - 
120° = 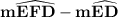
120° = 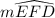 - (360° -
- (360° -
120° = 2·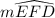 - 360°
- 360°
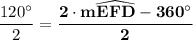
Which gives;
60° = 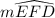 - 180°
- 180°
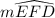 = 60° + 180° = 240°
= 60° + 180° = 240°
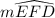 = 240°
= 240°
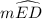 = 360° -
= 360° - 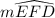 = 360° - 240° = 120°
= 360° - 240° = 120°
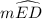 = 120°
= 120°
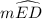 = 2 × m∠EFD angle subtended by an arc at the center is twice the angle subtended at the circumference
= 2 × m∠EFD angle subtended by an arc at the center is twice the angle subtended at the circumference
∴ 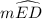 = 120° = 2 × m∠EFD
= 120° = 2 × m∠EFD
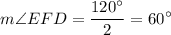
Therefore;
m∠EFD = m∠EGD = m∠G = 60°
m∠EGD = 60°
m∠EFD ≅ m∠EGD by definition of congruency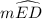 = m∠ECD by definition of the measure of an arc
= m∠ECD by definition of the measure of an arc
∴ 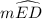 = 120° = m∠ECD
= 120° = m∠ECD
∴ m∠ECD ≠ m∠EGD = 60°
m∠ECD 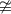 m∠EGD
m∠EGD
Given that m∠EFD = 60°, and ΔEFD is an isosceles triangle, we have;
∠DEF = ∠FDE
∠DEF + ∠FDE = 180° - 60° = 120°
∴ ∠DEF = ∠FDE = 60°
Therefore;
ΔEFD is an equilateral triangle (all angles are equal to 60°)
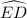 =
= 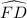 Equal chord subtend equal minor arcs theorem
Equal chord subtend equal minor arcs theorem
Therefore;
 by definition of congruency
by definition of congruency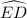 = 120° =
= 120° = 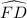
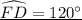
Learn more about circle theorems here:
link
 39
39 Step-by-step explanation:
In Quadrilateral GECD,
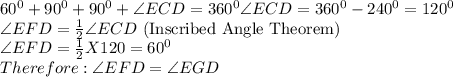
In Triangle EFD,
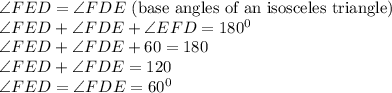
Similarly, In Triangle GED
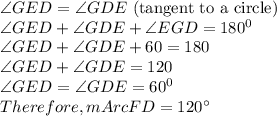
Finally, Arc ED is-congruent-to arc F D
The first, third and last options are true.
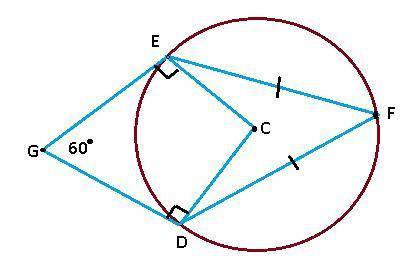
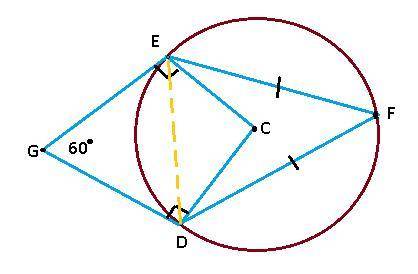
 39
39 Step-by-step explanation:
In Quadrilateral GECD,
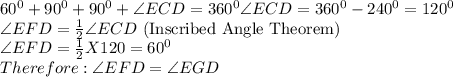
In Triangle EFD,
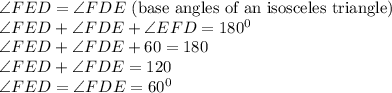
Similarly, In Triangle GED
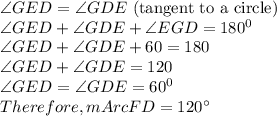
Finally, Arc ED is-congruent-to arc F D
The first, third and last options are true.


 87
87 A. Inscribed angles theorem
Step-by-step explanation:
A.inscribed angles theorem
B.third corollary to the inscribed angles theorem
C.central angle of a triangle has the same measure as its intercepted arc.
D.Angle formed by a tangent and a chord is half the measure of the intercepted arc.
Just took the unit test on edgen and got 100
 87
87 A. Inscribed angles theorem
Step-by-step explanation:
A.inscribed angles theorem
B.third corollary to the inscribed angles theorem
C.central angle of a triangle has the same measure as its intercepted arc.
D.Angle formed by a tangent and a chord is half the measure of the intercepted arc.
Just took the unit test on edgen and got 100
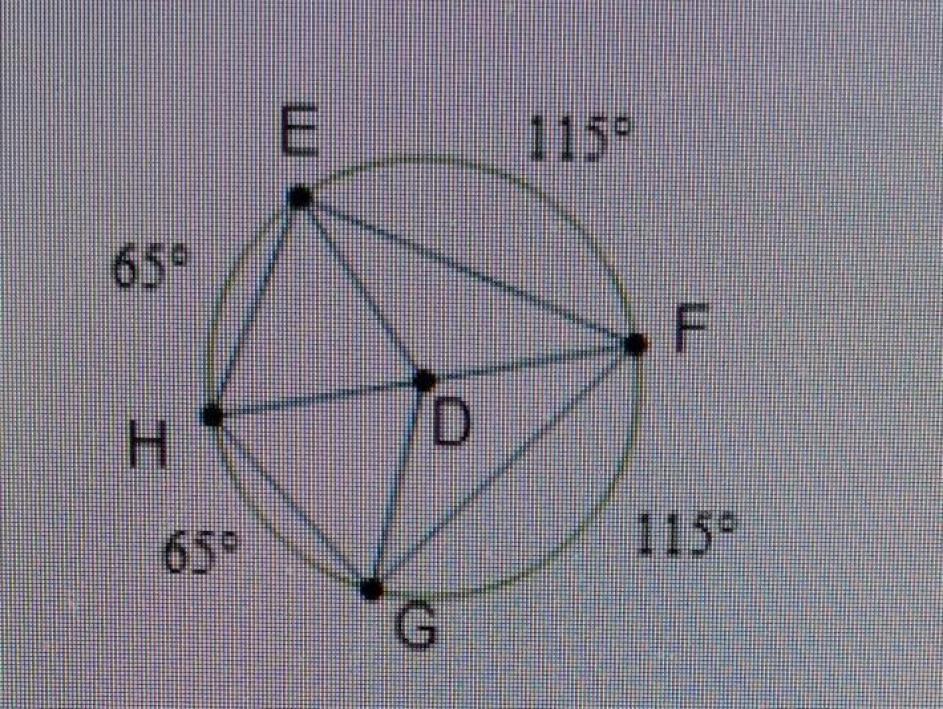
 6
6 inscribed angle theorem, gjh, substitution property
Options:
a. <EDH and <EDF
b. <EDF and <FDG
c. <FDG and <GDH
d. <GDH and <EDF
Answer:
b. <EDF and <FDG
Step-by-step explanation:
In geometry, two figures or objects are congruent if they have the same shape and size, or if one has the same shape and size as the mirror image of the other.
They have the same shape and size and angles. Also you can see that they are symmetric.
 14
14 A. 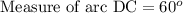
B. 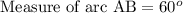
C. 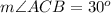
D. 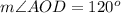
E. 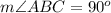
F. 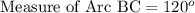
Step-by-step explanation:
We have been given that the diameter AC of circle O is 24 cm. Arcs AB and CD are congruent. Angle DOC = 60° .
A. Since we know that the degree measure of an arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that intercepts the arc.
We can see that angle DOC is central angle and 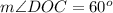 and arc DC subtends to central angle, therefore, the measure of arc DC will be 60 degrees.
and arc DC subtends to central angle, therefore, the measure of arc DC will be 60 degrees.
B. Since we are told that arcs AB and CD are congruent and measure of arc DC is 60 degrees, therefore, measure of arc AB will be 60 degrees as well.
C. The Inscribed Angle Theorem states that the measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc. Measure of Arc AB is 60 degrees, so by inscribed angle theorem the measure of angle ACB will be half the measure of AB.
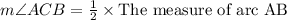
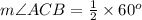
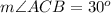
Therefore, measure of angle ACB will be 30 degrees.
D. We can see that angle DOC and AOD form a linear pair of angles, so they will add up-to 180 degrees.
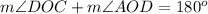
Upon substituting measure of angle DOC we will get,
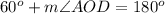
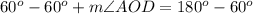
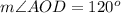
Therefore, measure of angle AOD will be 120 degrees.
E. Since we know that angle inscribed in a semicircle is always a right angle. We can see that angle ABC is angle inscribed in the semicircle as AC is the diameter of our given circle, therefore, measure of angle ABC will be 90 degrees.
F. Since we know that arc measure of a semicircle is 180 degrees. We can see that arc ABC is arc of the semicircle, so we can set an equation as:
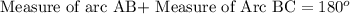
Upon substituting measure of arc AB we will get,
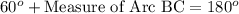
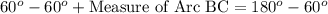
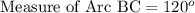
Therefore, measure of arc BC is 120 degrees.
 14
14 A. 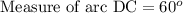
B. 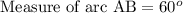
C. 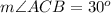
D. 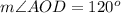
E. 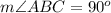
F. 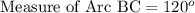
Step-by-step explanation:
We have been given that the diameter AC of circle O is 24 cm. Arcs AB and CD are congruent. Angle DOC = 60° .
A. Since we know that the degree measure of an arc is equal to the measure of the central angle that intercepts the arc.
We can see that angle DOC is central angle and 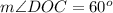 and arc DC subtends to central angle, therefore, the measure of arc DC will be 60 degrees.
and arc DC subtends to central angle, therefore, the measure of arc DC will be 60 degrees.
B. Since we are told that arcs AB and CD are congruent and measure of arc DC is 60 degrees, therefore, measure of arc AB will be 60 degrees as well.
C. The Inscribed Angle Theorem states that the measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc. Measure of Arc AB is 60 degrees, so by inscribed angle theorem the measure of angle ACB will be half the measure of AB.
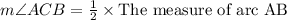
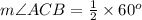
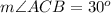
Therefore, measure of angle ACB will be 30 degrees.
D. We can see that angle DOC and AOD form a linear pair of angles, so they will add up-to 180 degrees.
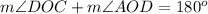
Upon substituting measure of angle DOC we will get,
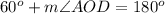
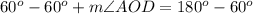
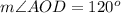
Therefore, measure of angle AOD will be 120 degrees.
E. Since we know that angle inscribed in a semicircle is always a right angle. We can see that angle ABC is angle inscribed in the semicircle as AC is the diameter of our given circle, therefore, measure of angle ABC will be 90 degrees.
F. Since we know that arc measure of a semicircle is 180 degrees. We can see that arc ABC is arc of the semicircle, so we can set an equation as:
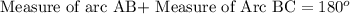
Upon substituting measure of arc AB we will get,
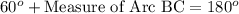
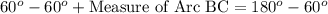
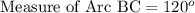
Therefore, measure of arc BC is 120 degrees.

It will provide an instant answer!
