 7
7  7
7  6
6 #1) d. ΔJKL is not a right triangle because no two of its sides are perpendicular; #2) -1/3, 3, -7, is, two of these slopes have a product of -1; #3) a. Quadrilateral DEFG is a rhombus because opposite sides are parallel and all four sides have the same length; #4) 1, -1/6, 1, -2/5, is not, only one pair of opposite sides is parallel; #5) c. Quadrilateral PQRS is not a rectangle because it has only one right angle.
Step-by-step explanation:
#1) The slope of any line segment is found using the formula
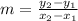
For JK, this gives us (1-1)/(-5-0) = 0/-5 = 0. For KL this gives us (1--5)/(0-2) = 6/-2 = -3. For LJ this gives us (-5-1)/(2--5) = -6/7. None of these slopes are negative reciprocals, so none of the angles are right angles and this is not a right triangle.
#2) The slope of JK is (2-1)/(0-3) = 1/-3 = -1/3. The slope of KL is (1--5)/(3-1) = 6/2 = 3. The slope of LJ is (2--5)/(0-1) = 7/-1 = -7. Two of these slopes have a product of -1, 3 and -1/3. This means they are negative reciprocals so this has a right angle; this means JKL is a right triangle.
#3) The slope of DE is (5-4)/(-2-2) = 1/-4 = -1/4. The slope of EF is (4-0)/(2-0) = 4/2 = 2. The slope of FG is (0-1)/(0--4) = -1/4. The slope of GD is (1-5)/(-4--2) = -4/-2 = 2. Opposite sides have the same slope so they are parallel.
Next we use the distance formula to find the length of each side:
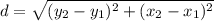
Using our points, the length of DE is
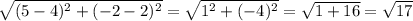
The length of EF is
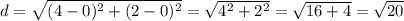
The length of FG is
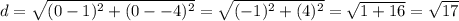
The length of GD is
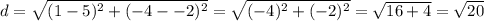
Opposite sides have the same length and are parallel, so this is a parallelogram.
#4) The slope of AB is (-1-2)/(-4--1) = -3/-3 = 1. The slope of BC is (2-1)/(-1-5) = 1/-6 = -1/6. The slope of CD is (1--3)/(5-1) = 4/4 = 1. The slope of DA is (-3--1)/(1--4) = -2/5. Only one pair of opposite sides is parallel, so this is not a parallelogram.
#5) The slope of PQ is (2-4)/(-4-3) = -2/-7 = 2/7. The slope of QR is (4-0)/(3-5) = 4/-2 = -2. The slope of RS is (0--2)/(5--3) = 2/8 = 1/4. The slope of SP is (-2-2)/(-3--4) = -4/1 = -4. Only one pair of sides has slopes that are negative reciprocals; this means this figure only has 1 right angle, so it is not a rectangle.
 12
12 a. Quadrilateral PQRS is not a rectangle because it has only one right angle.
Step-by-step explanation:
 12
12 a. Quadrilateral PQRS is not a rectangle because it has only one right angle.
Step-by-step explanation:
 6
6 #1) d. ΔJKL is not a right triangle because no two of its sides are perpendicular; #2) -1/3, 3, -7, is, two of these slopes have a product of -1; #3) a. Quadrilateral DEFG is a rhombus because opposite sides are parallel and all four sides have the same length; #4) 1, -1/6, 1, -2/5, is not, only one pair of opposite sides is parallel; #5) c. Quadrilateral PQRS is not a rectangle because it has only one right angle.
Step-by-step explanation:
#1) The slope of any line segment is found using the formula
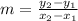
For JK, this gives us (1-1)/(-5-0) = 0/-5 = 0. For KL this gives us (1--5)/(0-2) = 6/-2 = -3. For LJ this gives us (-5-1)/(2--5) = -6/7. None of these slopes are negative reciprocals, so none of the angles are right angles and this is not a right triangle.
#2) The slope of JK is (2-1)/(0-3) = 1/-3 = -1/3. The slope of KL is (1--5)/(3-1) = 6/2 = 3. The slope of LJ is (2--5)/(0-1) = 7/-1 = -7. Two of these slopes have a product of -1, 3 and -1/3. This means they are negative reciprocals so this has a right angle; this means JKL is a right triangle.
#3) The slope of DE is (5-4)/(-2-2) = 1/-4 = -1/4. The slope of EF is (4-0)/(2-0) = 4/2 = 2. The slope of FG is (0-1)/(0--4) = -1/4. The slope of GD is (1-5)/(-4--2) = -4/-2 = 2. Opposite sides have the same slope so they are parallel.
Next we use the distance formula to find the length of each side:
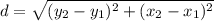
Using our points, the length of DE is
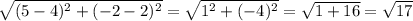
The length of EF is
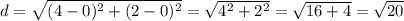
The length of FG is
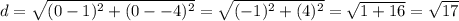
The length of GD is
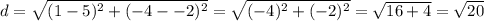
Opposite sides have the same length and are parallel, so this is a parallelogram.
#4) The slope of AB is (-1-2)/(-4--1) = -3/-3 = 1. The slope of BC is (2-1)/(-1-5) = 1/-6 = -1/6. The slope of CD is (1--3)/(5-1) = 4/4 = 1. The slope of DA is (-3--1)/(1--4) = -2/5. Only one pair of opposite sides is parallel, so this is not a parallelogram.
#5) The slope of PQ is (2-4)/(-4-3) = -2/-7 = 2/7. The slope of QR is (4-0)/(3-5) = 4/-2 = -2. The slope of RS is (0--2)/(5--3) = 2/8 = 1/4. The slope of SP is (-2-2)/(-3--4) = -4/1 = -4. Only one pair of sides has slopes that are negative reciprocals; this means this figure only has 1 right angle, so it is not a rectangle.
 56
56 Quadrilateral PQRS is not a rectangle because it has only one right angle.
 15
15 Step-by-step explanation:
Given: Quadrilateral PQRS is a rectangle.
To prove: PR = QS
Proof: 1. Quadrilateral PQRS is a rectangle(Given).
2. Rectangle PQRS is a parallelogram (Definition of a rectangle).
3. QP ≅ RS QR ≅ PS (Opposite angles of parallelogram are equal).
4. m∠QPS = m∠RSP = 90° (definition of a rectangle)
5. Δ PQS ≅ ΔSRP (SAS criterion for congruence)
6. PR ≅ QS (Corresponding sides of congruent triangles are congruent).
7. PR = QS (Congruent line segments have equal measures).
 15
15 Step-by-step explanation:
Given: Quadrilateral PQRS is a rectangle.
To prove: PR = QS
Proof: 1. Quadrilateral PQRS is a rectangle(Given).
2. Rectangle PQRS is a parallelogram (Definition of a rectangle).
3. QP ≅ RS QR ≅ PS (Opposite angles of parallelogram are equal).
4. m∠QPS = m∠RSP = 90° (definition of a rectangle)
5. Δ PQS ≅ ΔSRP (SAS criterion for congruence)
6. PR ≅ QS (Corresponding sides of congruent triangles are congruent).
7. PR = QS (Congruent line segments have equal measures).
 54
54 opposite sides in rectangle are congruent.
Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that Quadrilateral PQRS is a rectangle.
Since opposite sides of rectangle are congruent.
Therefore , QP ≅ RS, QR ≅ PS
Therefore, the reason for "QP ≅ RS, QR ≅ PS" in this proof is "opposite sides in rectangle are congruent."
hence, the reason for the third step in this proof is "opposite sides in rectangle are congruent."

It will provide an instant answer!
