These are 14 questions and 14 answers.
Since this exceeds the limit and I had to delete the last questions and I copied all the answers to a file that is attache. See the attachment with all the answers.
1) Question 1. Find the first six terms of the sequence: a1 = -6, an = 4 • an-1
option D) -6, -24, -96, -384, -1536, -6144
Explanation:
A(1) = - 6
A(n) = 4 * A(n-1)
n A(n)
1 - 6
2 4 * (-6) = - 24
3 4 * (-24) = - 96
4 4 * (-96) = - 384
5 4 * (-384) = - 1536
6 4 * ( -1536) = -6144
So, the first six terms are: -6, - 24, - 96, - 384, - 1536, - 6144.
2) Question 2: Find an equation for the nth term of the
arithmetic sequence.
-15, -6, 3, 12, ...
option D) - 15 + 9(n - 1)
Explanation:
1. find the difference between the consecutive terms:
-6 - (-15) = -6 + 15 = 9
3 - (-6) = 3 + 6 = 9
12 - 3 = 9
So, the difference is 9, and you can find any term adding 9 to the previous.
2. Since the first term is - 15, you have:
First term, A1 = - 15 + 9(0) = - 15
Second term, A2 = - 15 + 9(1) = - 6
Third term, A3 = -15 + 9(2) = - 15 + 18 = 3
Fourth term, A4 = - 15 + 9(3) = - 15 + 27 = 12
3. So, the general formula is An = - 15 + 9 (n - 1), which is the option D)
3) Question 3. Find an equation for the nth term of the arithmetic sequence A14 = - 33, A15 = 9.
option B) An = - 579 + 42(n - 1)
Explanation:
1) Find the difference: 9 - (-33) = 9 + 33 = 42
2) A15 = A1 + 42 * (15 - 1)
=> A1 = A15 - 42(15 - 1)
A1 = A15 - 42(14)
A1 = 9 - 588 = - 579
Therefore, the formula es An = - 579 + 42(n - 1)
4) Question 4. Determine whether the sequence converges or
diverges. If it converges, give the limit.
48, 8, 4/3, 2/9, ...
the sequence converges to 288/5
Explanation:
That is a geometric sequence.
The ratio is 1/6: 8/48 = 1/6; (4/3) / 8 = 4/24 = 1/6; (2/9)/(4/3) = 6/36 = 1/6.
The convergence criterium is that if |ratio| < 1 then the series, this is the sum of all the terms, converge to: A1 / (1 - ratio)
Then the limit 48 / (1 - 1/6) = 48 / (5/6) = 48*6 / 5 = 288/5
5) Question 5. Find an equation for the nth term of the sequence.
-3, -12, - 48, -192
- 3 * (4)^(n-1)
Explanation: clearly any term (from the second) is the previous term multiplied by 4.
The first term is -3
The second term is -3(4) = - 12
The third term is -3(4)(4)= - 48
The fourth term is - 3 (4)(4)(4) = - 192
So, the general formula for the nth term is -3 * 4^ (n-1)
6) Question 6. Find an equation for the nth term of a geometric
sequence where the second and fifth terms are -21 and 567, respectively.
An =7 * (-3)^(n-1)
Explanation:
1) The fith term is the second term * (ratio)^3: A5 = A3 * (r)^3
2) A5 = 567, A2 = - 21 => r^3 = A5 / A2 = - 567 / 21 = - 27
=> r = ∛(-27) = - 3
3) So the first term is A1 = A2 / r = -21 / -3 = 7
4) The general formula is
An =7 * (-3)^(n-1)
7) Question 7. Write the sum using summation notation,
assuming the suggested pattern continues.
5 - 15 + 45 - 135 + ...
option B) summation of five times negative three to the
power of n from n equals zero to infinity
Explanation:
5 = 5
-15 = 5 (-3)
45 = 5(-3)^2
-135 = 5(-3)^3
=> 5 + 5(-3) + 5(-3)^2 + 5(-3)^3+
Using the summation notation that is:
∞
∑ (5)(-3)^n
n=0
Which means summation of five times negative three to the
power of n from n equals zero to infinity
8) Question 8. Write the sum using summation notation,
assuming the suggested pattern continues.
-9 - 3 + 3 + 9 + ... + 81
option A) summation of the quantity negative nine plus
six n from n equals zero to fifteen
Explanation:
Find the difference:
-3 - (-9) = - 3 + 9 = 6
3 - (-3) = 3 + 3 = 6
9 - 3 = 6
First term: - 9
Second term: - 9 + 6(1)
Third term: - 9 + 6(2)
nth term = - 9 + (n -1)
Summation = [- 9] + [- 9 + 6(1) + [-9 + 6(2)] + [-9 + 6(3) ]+ [-9 + 6(15) ]
Using summation notation:
15
∑ [-9 + 6n]
n=0
which means summation of the quantity negative nine plus
six n from n equals zero to fifteen.
9) Question 9.
Write the sum using summation notation, assuming the suggested pattern
continues.
64 + 81 + 100 + 121 + ... + n2 + ...
A) summation of n squared from n equals eight to infinity
Explanation:
64 = 8^2
81 = 9^2
100 = 10^2
121 = 11^2
n^2
=>
∞
∑ n^2
n=8
which means summation of n squared from n equals eight to
infinity
10) Question 10. Find the sum of the arithmetic sequence.
17, 19, 21, 23, ..., 35
260
Explanation:
The difference is 2:
The sum is: 17 + 19 + 21 + 23 + 25 + 27 + 29 + 31 + 33 + 35.
You can use the formula for the sum of an arithmetic sequence:
(A1 + An) * n / 2 = (17 + 35)*10/2 = 260
11) Question 11. Find the sum of the geometric sequence.
1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16
option D) 31/16
Explanation:
You can either sum the 5 terms or use the formula for the partial sum of a geometric sequence.
The formula is: Sum = A * ( 1 - r^n) / (1 - r)
Here A = 1, r = 1/2, and n = 5 => Sum = 1 * (1 - (1/2)^5 ) / (1 - 1/2) =
= [ 1 - 1/32] / [1/2] = [31/32] / [1/2] = 31 / 16
 2
2  100
100  2
2  2
2 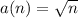
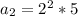
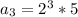
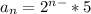
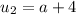
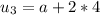
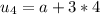
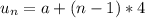
 2
2 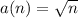
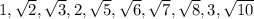
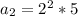
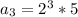
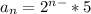
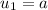
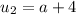
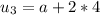
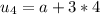
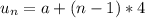
 21
21  100
100  11
11 
