 37
37  37
37  5
5 answers in order C,A,B,D,because the reactants only partially ionize in the solution,none of these( SO4 2- is a strong one),none of these( all are weak),same(beacause both Ka and Kb values are equal in those subtances),di,mono,tri,mono,mono,mono,di,di,mono,Na2Be(OH)4(aq)...
Explanation:
this quiz doesnt worth my time...but have a nice day.
 5
5 answers in order C,A,B,D,because the reactants only partially ionize in the solution,none of these( SO4 2- is a strong one),none of these( all are weak),same(beacause both Ka and Kb values are equal in those subtances),di,mono,tri,mono,mono,mono,di,di,mono,Na2Be(OH)4(aq)...
Explanation:
this quiz doesnt worth my time...but have a nice day.
 2
2 See below
Explanation:
a) Adding HCl
HBTB is yellow in acid solution.
b) Adding NaOH
HBTB is blue in basic solution.
c) Explanation
HBTB is a weak acid in which the undissociated and ionized forms have different colours.
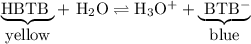
Around pH 7 , the indicator consists of roughly equal amounts of the yellow and blue forms, so it appears green
According to Le Châtelier's Principle, if you apply a stress to a system at equilibrium, it will respond in a way that will relieve the stress.
When you added HCl, you increased the concentration of H₃O⁺. The system responded in a way that would decrease the H₃O⁺. That is, the position of equilibrium shifted to the left and produced more of the yellow form.
When you added NaOH, the base removed some of the H₃O⁺. The system responded in a way that would increase the H₃O⁺. That is, the position of equilibrium shifted to the right and produced more of the blue form
 5
5  2
2 See below
Explanation:
a) Adding HCl
HBTB is yellow in acid solution.
b) Adding NaOH
HBTB is blue in basic solution.
c) Explanation
HBTB is a weak acid in which the undissociated and ionized forms have different colours.
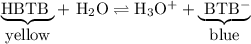
Around pH 7 , the indicator consists of roughly equal amounts of the yellow and blue forms, so it appears green
According to Le Châtelier's Principle, if you apply a stress to a system at equilibrium, it will respond in a way that will relieve the stress.
When you added HCl, you increased the concentration of H₃O⁺. The system responded in a way that would decrease the H₃O⁺. That is, the position of equilibrium shifted to the left and produced more of the yellow form.
When you added NaOH, the base removed some of the H₃O⁺. The system responded in a way that would increase the H₃O⁺. That is, the position of equilibrium shifted to the right and produced more of the blue form
 5
5  8
8  8
8 
It will provide an instant answer!
