 2
2 Step-by-step explanation:
At first, lets find the distance from one point to the other.
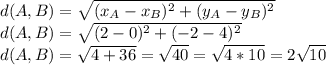
The same way, you can find that:
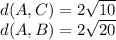
Since the triangle has only its two sides equal to each other (AB = AC),
it's an isosceles one.
As long as the angles are concerned, we gotta "cheat". In other words, we see that:
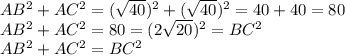
By the inverse of pythagorean theorem, we know that if the above equation holds, then we have a right-angled triangle. That is to say that,
A = 90
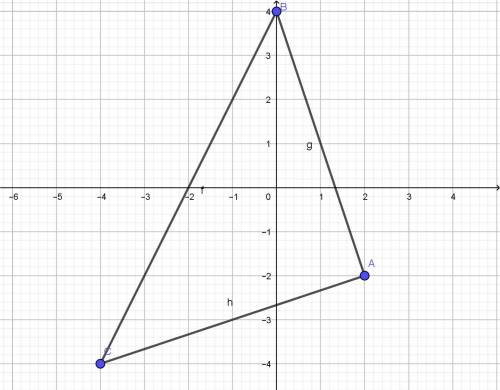
Since its an isosceles triangle, AB = AC,
B = C = (180 - A)/2 = 45 degrees
 2
2 Step-by-step explanation:
At first, lets find the distance from one point to the other.
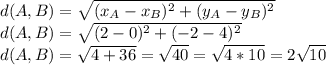
The same way, you can find that:
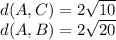
Since the triangle has only its two sides equal to each other (AB = AC),
it's an isosceles one.
As long as the angles are concerned, we gotta "cheat". In other words, we see that:
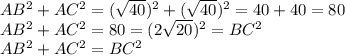
By the inverse of pythagorean theorem, we know that if the above equation holds, then we have a right-angled triangle. That is to say that,
A = 90
Since its an isosceles triangle, AB = AC,
B = C = (180 - A)/2 = 45 degrees

 26
26 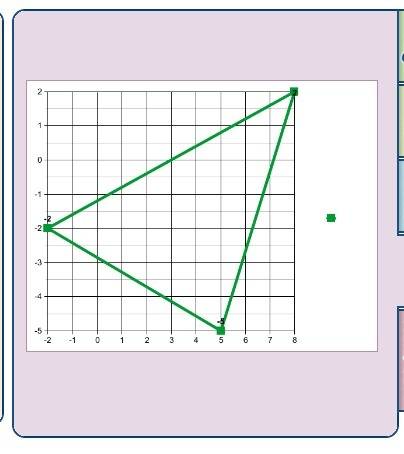
 5
5  1
1 The triangle would be isosceles.
Step-by-step explanation:
hope this helps~
 19
19 ΔPQR is an equilateral triangle.
Step-by-step explanation: The vertices of a triangle PQR are given as follows:
P(0, 0), Q(6, 0) and R(3, 3√3).
We are to find the type of the triangle by finding the lengths of its three sides.
The lengths of the three sides PQ, QR and PR are calculated using distance formula as follows:
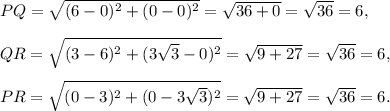
Therefore, PQ = QR = PR.
All the sides of the triangle PQR are equal, and so the triangle is equilateral.
Thus, ΔPQR is an equilateral triangle.
 20
20  26
26 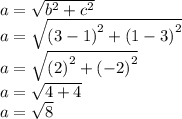
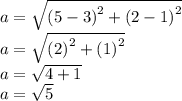
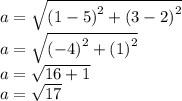
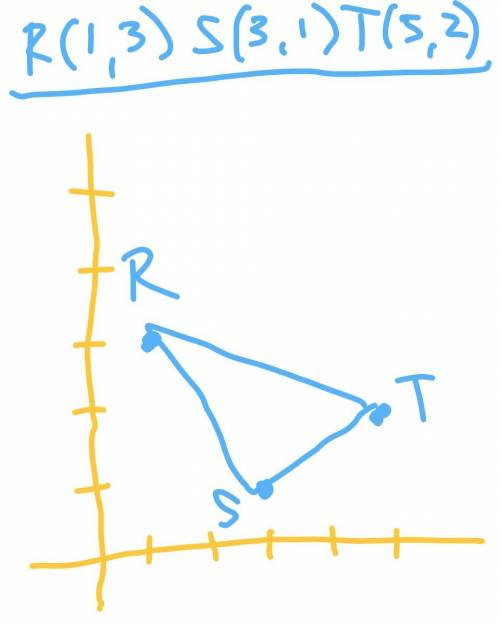
 5
5 Step-by-step explanation:
KL = 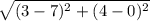 = 4√2
= 4√2
LM = 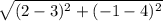 = √26
= √26
KM = 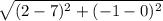 = √26
= √26
ΔKLM is isosceles.
 13
13 >regular triangle, we call equilateral triangles regular polygons.
>isosceles, as an equilaterial triangle is a specific type of isosceles due to more than one side being of equal length and angle.
>equilateral, where all sides and angles are the same.
>acute, as all 3 angles are less than 90
>equiangular. equilateral triangles are also described as equiangular.
Step-by-step explanation:
Just the five ways above can describe the polygon shown, as the angles of a scalene triangle are unequal. as are their sides, equilaterial have same sides and angles. Obtuse have angles larger than 90deg less than 180 deg.
Whilst irregular are triangles and shapes that have uneven sides and are not right or isosceles.
Right triangles have one angle that is exactly 90 deg.

It will provide an instant answer!
