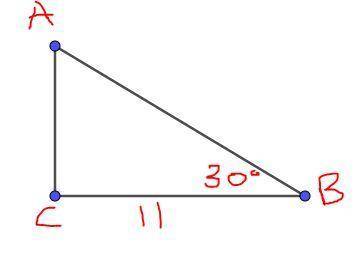
1. The given triangle ABC, has a right angle at C, BC=11, and 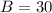
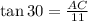
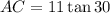
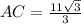
Ans: A
2. The reference angle is the angle the terminal side makes with x-axis.
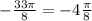
This implies that, 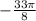 has a reference angle of
has a reference angle of 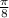 .
.
Ans: C
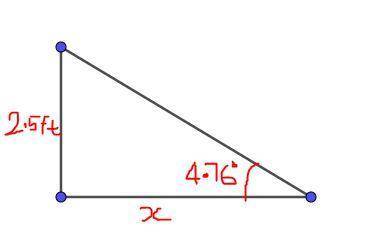
3. Let x be the shortest distance the ramp can span.
From the diagram; 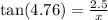
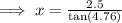
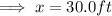
Ans:B
4. Use the Pythagorean identity: 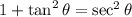 .
.
If 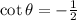 ,then
,then 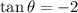
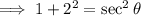
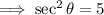
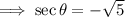 , In QII, the secant ratio is negative.
, In QII, the secant ratio is negative.
Ans:C
5. We have 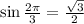
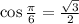
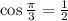
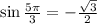
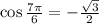
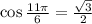
Ans:A and D
6. The given function that is equivalent to 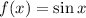 is
is 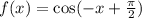 .
.
When we reflect the graph of 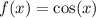 in the y-axis and shift it to the left by
in the y-axis and shift it to the left by 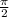 units, it coincides with graph of
units, it coincides with graph of 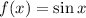 .
.
Ans:C
7. The function 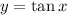 is a one-to-one function on the interval
is a one-to-one function on the interval ![[-\frac{\pi}{2},\frac{\pi}{2}]](/tpl/images/0029/3850/8b799.png)
When we restrict the domain of 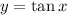 on
on ![[-\frac{\pi}{2},\frac{\pi}{2}]](/tpl/images/0029/3850/8b799.png) it becomes an invertible function.
it becomes an invertible function.
Ans: C
8. The given function is 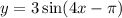
The horizontal shift is given by 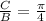
The direction of the shift is to the right.
Ans:D
9. 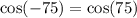 by the symmetric property of even functions.
by the symmetric property of even functions.
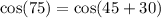
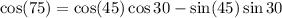
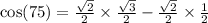
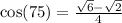
Ans: B
10. Recall the cosine rule: 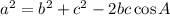
Let the angle measure opposite to the longest side be A, then a=19,b=17, and c=15.
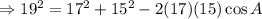
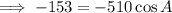
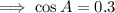
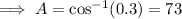
Ans:B
11. We want to solve 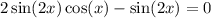 on the interval;
on the interval;
![[-\frac{\pi}{2},\frac{\pi}{2}]](/tpl/images/0029/3850/8b799.png)
Factor: 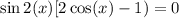
Either 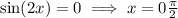
Or 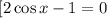 This means that
This means that 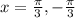
Therefore required solution is 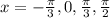
Ans:D
12. Use the relation: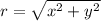 and
and 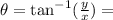
The given rectangular coordinate is (1,-2)
This implies that: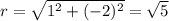
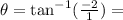 This means
This means 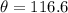 or
or 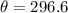
The polar forms are: 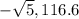 and
and 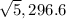
Ans: B and C
13. The polar equation that represents an ellipse is
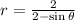 .
.
When written in standard form; 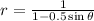 .
.
The eccentricity is 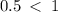 .
.
Therefore the 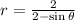 is an ellipse.
is an ellipse.
Ans: B
14. The DeMoivre’s Theorem states that;
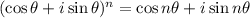
This implies that:
![[2(\cos \frac{\pi}{9}+i\sin \frac{\pi}{9})]^3=2^3\cos 3\times \frac{\pi}{9}+i\sin 3\times \frac{\pi}{9})](/tpl/images/0029/3850/de0fb.png)
![[2(\cos \frac{\pi}{9}+i\sin \frac{\pi}{9})]^3=8(frac{2}{2})+i8(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2})=4+4\sqrt{3}i](/tpl/images/0029/3850/dad44.png)
Ans: A
15. Let the initial point be (x,y), Then 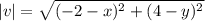 .
.
If x=-8, and y=-4.
Then, 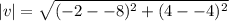 .
.
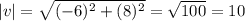 .
.
Ans: B
16. We find the dot product to see if it is zero.
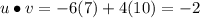
Since the dot product is not zero the vectors are not orthogonal
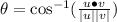
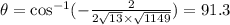
Ans:B
17. Given v=5i+4j, w=2i-3j.
u=v+w
Add corresponding components
This implies u=(5i+4j)+(2i-3j)
u=(5i+2i+4j-3j)
u=7i+j
Ans:B
See attachment.