 1
1 Probability = 0.8444
Step-by-step explanation:
To solve this problem, we need to obtain the z-value which corresponds to the probability that the mean of a sample of 84 computers would differ from the population mean by less than 1.39 months
Let x' denote the mean life of the computer.
Mean = 88 months
Variance = 81
Thus, standard deviation = √81 = 9
Thus, we obtain;
P(|x - μ| < 1.39) = P(-1.39 > x < 1.39)
For x' = - 1.39,
z = -1.39/(9/√84)
z = -1.39/0.982
z = -1.42
For x' = 1.39,
z = 1.39/(9/√84)
z = 1.39/0.982
z = 1.42
Thus, P(|x - μ| < 1.39) =
P(−1.42 < z < 1.42)
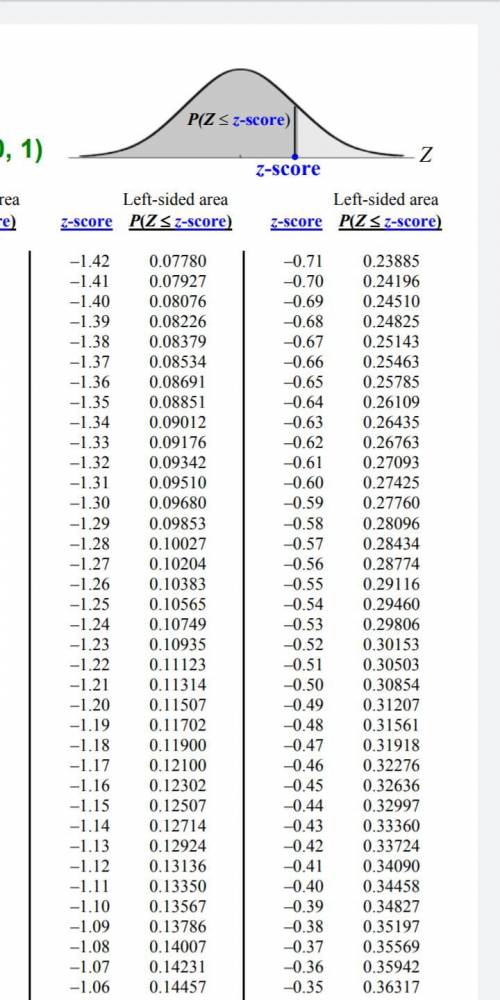
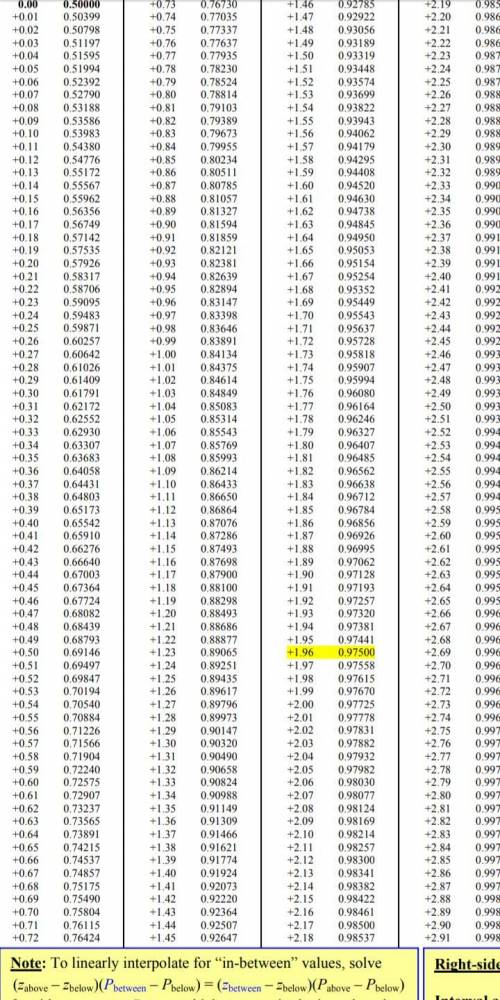
From the Z-distribution tables i attached, we obtain ;
0.92220 - 0.07780 = 0.8444
P(X<118.81)=0.0803
Step-by-step explanation:
Assuming the distribution for the mean life is approximately normal, with mean 120 months and variance 64 months^2, we can calculate the parameters for a sampling distribution with sample size = 89 computers.
The sampling distribution mean will be equal to the mean for a single computer:
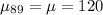
The standard deviation will be adjusted by the sample size as:
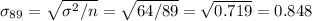
With these parameters, we can calculate the z-score for X=118.81.
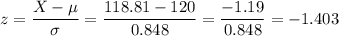
Then, the probability that the mean of a sample of 89 computers is less than 118.81 months is:
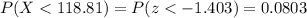
 1
1 P(x < 117.13) = 0.0033
Step-by-step explanation:
Let us assume that the mean life of the computers are normally distributed, we would apply the formula for normal distribution which is expressed as
z = (x - µ)/σ/√n
Where
x = lifetime of the computers in months.
µ = mean lifetime
σ = standard deviation
n represents the number of samples
From the information given,
µ = 120 months
σ = 10 months
n = 90
The probability that the mean life of a sample of 90 computers would be less than 117.13 months is expressed as
P(x < 117.13)
For x = 117.13
z = (117.3 - 120)/10/√90
z = - 2.87/1.0541 = - 2.72
Looking at the normal distribution table, the probability corresponding to the z score is 0.0033
 1
1 0.1788
Step-by-step explanation:
As per given , we have
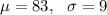
Let x be the random variable that represents the life of a computer.
Sample size : n= 78
Then, the z-score corresponds to x= 82.06 will be :-
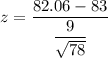 [∵
[∵ 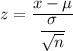 ]
]
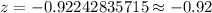
Required probability ( using standard z-value table ) :-
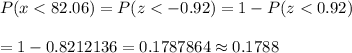
Hence, the probability that the mean of a sample of 78 computers would be less than 82.06 months = 0.1788
P(X<118.81)=0.0803
Step-by-step explanation:
Assuming the distribution for the mean life is approximately normal, with mean 120 months and variance 64 months^2, we can calculate the parameters for a sampling distribution with sample size = 89 computers.
The sampling distribution mean will be equal to the mean for a single computer:
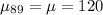
The standard deviation will be adjusted by the sample size as:
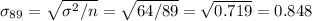
With these parameters, we can calculate the z-score for X=118.81.
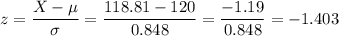
Then, the probability that the mean of a sample of 89 computers is less than 118.81 months is:
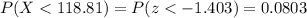
 1
1 Probability = 0.8444
Step-by-step explanation:
To solve this problem, we need to obtain the z-value which corresponds to the probability that the mean of a sample of 84 computers would differ from the population mean by less than 1.39 months
Let x' denote the mean life of the computer.
Mean = 88 months
Variance = 81
Thus, standard deviation = √81 = 9
Thus, we obtain;
P(|x - μ| < 1.39) = P(-1.39 > x < 1.39)
For x' = - 1.39,
z = -1.39/(9/√84)
z = -1.39/0.982
z = -1.42
For x' = 1.39,
z = 1.39/(9/√84)
z = 1.39/0.982
z = 1.42
Thus, P(|x - μ| < 1.39) =
P(−1.42 < z < 1.42)
From the Z-distribution tables i attached, we obtain ;
0.92220 - 0.07780 = 0.8444


 1
1 0.1788
Step-by-step explanation:
As per given , we have
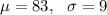
Let x be the random variable that represents the life of a computer.
Sample size : n= 78
Then, the z-score corresponds to x= 82.06 will be :-
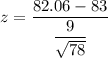 [∵
[∵ 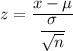 ]
]
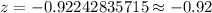
Required probability ( using standard z-value table ) :-
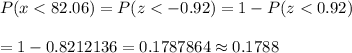
Hence, the probability that the mean of a sample of 78 computers would be less than 82.06 months = 0.1788
 1
1 P(x < 117.13) = 0.0033
Step-by-step explanation:
Let us assume that the mean life of the computers are normally distributed, we would apply the formula for normal distribution which is expressed as
z = (x - µ)/σ/√n
Where
x = lifetime of the computers in months.
µ = mean lifetime
σ = standard deviation
n represents the number of samples
From the information given,
µ = 120 months
σ = 10 months
n = 90
The probability that the mean life of a sample of 90 computers would be less than 117.13 months is expressed as
P(x < 117.13)
For x = 117.13
z = (117.3 - 120)/10/√90
z = - 2.87/1.0541 = - 2.72
Looking at the normal distribution table, the probability corresponding to the z score is 0.0033
Follows are the solution to this question:
Explanation:
Physical- Pablo: Its physical control includes tangible goods, machinery and inventory control, product quality. product quality. Its task of Carlos is to control work computers which our company know.
Human- Drishti: Human control includes recruiting, education, development, rewards, performance assessment, evaluation of performance, and evaluation of job satisfaction. Drishti hires an advisor here, which why he's under human control.
Informational- Michael: Knowledge control covers ecological and market research, process design, media affairs, economic predictions, and sales. To communicate or announce company activities with third stakeholders, Michael speaks to the media.
Financial- Jada: Financial control comprises financial planning, payments, transactions, or impact on the cash flow, cash, repayment schedule. Here, Jada worries about the payrolls which need to be paid.
Structural- Wen: Bureaucratic or autonomous institutional controls include governance or hierarchy. Wen claims the framework can therefore be assigned to a group with both the project.
Cultural- Malik: Cultural control includes several principles developed based on both the values and beliefs in an organization, which affects the working process performance level. In his new job, Malik discovers how his coworkers have higher quality and performance standards, the corporation's convictions.
Follows are the solution to this question:
Explanation:
Physical- Pablo: Its physical control includes tangible goods, machinery and inventory control, product quality. product quality. Its task of Carlos is to control work computers which our company know.
Human- Drishti: Human control includes recruiting, education, development, rewards, performance assessment, evaluation of performance, and evaluation of job satisfaction. Drishti hires an advisor here, which why he's under human control.
Informational- Michael: Knowledge control covers ecological and market research, process design, media affairs, economic predictions, and sales. To communicate or announce company activities with third stakeholders, Michael speaks to the media.
Financial- Jada: Financial control comprises financial planning, payments, transactions, or impact on the cash flow, cash, repayment schedule. Here, Jada worries about the payrolls which need to be paid.
Structural- Wen: Bureaucratic or autonomous institutional controls include governance or hierarchy. Wen claims the framework can therefore be assigned to a group with both the project.
Cultural- Malik: Cultural control includes several principles developed based on both the values and beliefs in an organization, which affects the working process performance level. In his new job, Malik discovers how his coworkers have higher quality and performance standards, the corporation's convictions.

It will provide an instant answer!
