Answer:
Answers given below:Step-by-step explanation:
1. The skater will never get any higher than 6 meters because he can't create any energy, since he has a certain amount of potential energy that is being converted to kinetic energy so he could move up the ramp and then converted again to potential energy when he is at 6 meters on the other side.
2. No. As when the skater is dropped onto the ramp from above, the potential energy decreases and the kinetic energy increases. Every time the skater bounces from the impact, thermal energy is gained, and both potential and kinetic energy are lost.
3. This means that internal energy of a system can be increased by adding heat into the system or by performing work on the system. As per the given problem, we can increase the height of the system.
4. As the skateboarder goes down the ramp, potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. Because of friction, some of the energy in the system is converted to heat energy. Once the kinetic energy is converted to heat, the energy cannot be converted back to the potential or kinetic energy in the system.
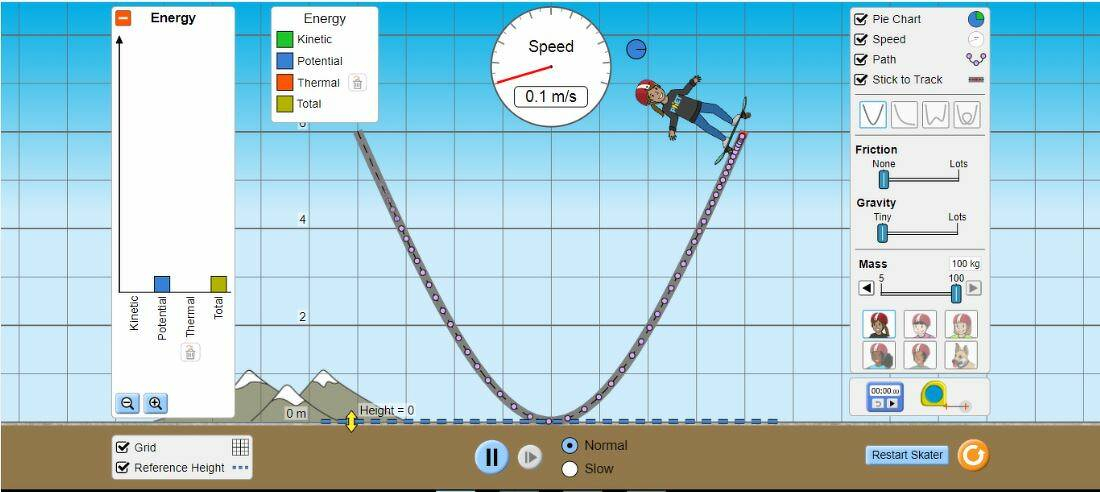
Without friection
with lots of friction
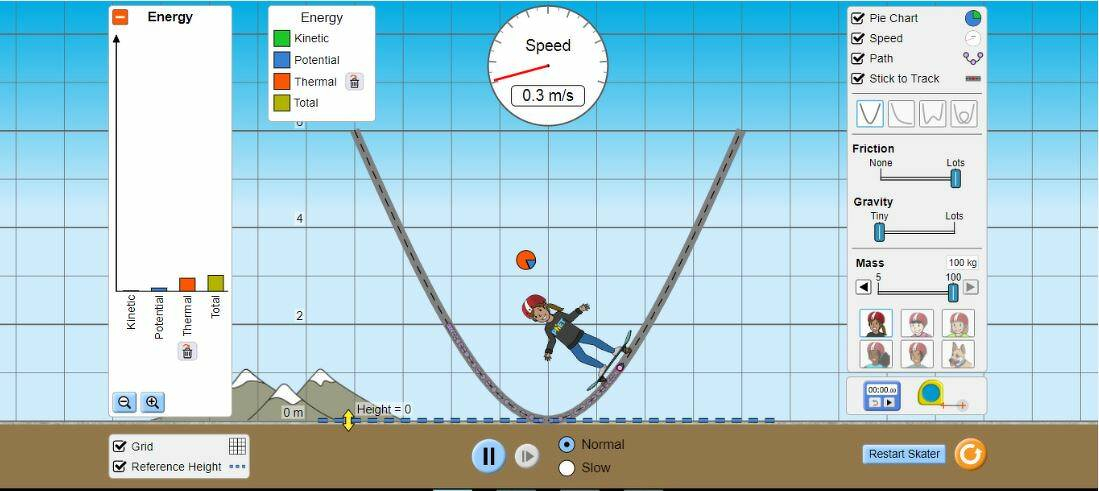
Question2
Along the path from left to right, no energy is converted to thermal energy since the track is frictionless. If no energy is lost, the skater will have enough energy to reach the same height he started with.
Question 3
The energy is being converted to thermal energy because the friction between the ramp and the skater causes heat. This means in real life that if the skater causes a lot of friction while skateboarding, he or she would be slower and have less energy on the ramp.