 1
1 Explanation:
1) is attached below
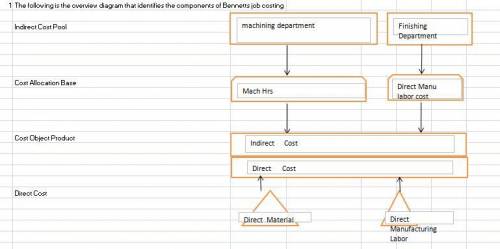
2) Budgeted manufacturing overhead rate :
In Machining Department = Manufacturing overhead cost / Machine hrs
= $9065000 /185,000 = $49 per machine hour
In Finishing Department = Manufacturing overhead cost / Direct Manufacturing labor cost
= $8,058000 / $3950,000 = 2.04
3) Machining Department overhead = $20 per machine hr * 100 hrs
= $2000
Finishing Department overhead = $1400 * 204% = $2856
Total manufacturing overhead = $4856
4).Total costs of Job 431:
Direct material - Machining Department = $14500
- Finishing Department = $4000
Direct manufacturing labor - Machining Department = $800
- Finishing Department = $1400
Manufacturing overhead = $4856
Total Cost = $25556
Cost per unit = $25556 / 100 = $255.56
5)
Actual manufacturing overhead machining finishing
Actual manufacturing overhead $12,010,000 $9,184,000
Manufacturing overhead allocated $11,760,000 $9,384,000
($49×240,000)(204%×4600,000)
Under allocated(over allocated) $250,000 $(200,000.00)
For plant as whole:
(12,010,000+$9184,000)-(11760,000+$9384,000)
50000 Under applied.
6) In machining department main focal points is machines , so machine hours is selected for this.In finishing department, labor cost is key area.so it is selected by the company .In both department key area is different so different cost drivers are selected for both departments.
 1
1 Explanation:
1) is attached below
2) Budgeted manufacturing overhead rate :
In Machining Department = Manufacturing overhead cost / Machine hrs
= $9065000 /185,000 = $49 per machine hour
In Finishing Department = Manufacturing overhead cost / Direct Manufacturing labor cost
= $8,058000 / $3950,000 = 2.04
3) Machining Department overhead = $20 per machine hr * 100 hrs
= $2000
Finishing Department overhead = $1400 * 204% = $2856
Total manufacturing overhead = $4856
4).Total costs of Job 431:
Direct material - Machining Department = $14500
- Finishing Department = $4000
Direct manufacturing labor - Machining Department = $800
- Finishing Department = $1400
Manufacturing overhead = $4856
Total Cost = $25556
Cost per unit = $25556 / 100 = $255.56
5)
Actual manufacturing overhead machining finishing
Actual manufacturing overhead $12,010,000 $9,184,000
Manufacturing overhead allocated $11,760,000 $9,384,000
($49×240,000)(204%×4600,000)
Under allocated(over allocated) $250,000 $(200,000.00)
For plant as whole:
(12,010,000+$9184,000)-(11760,000+$9384,000)
50000 Under applied.
6) In machining department main focal points is machines , so machine hours is selected for this.In finishing department, labor cost is key area.so it is selected by the company .In both department key area is different so different cost drivers are selected for both departments.

WoolCorp
1. Single Plantwide Factory Overhead Rate: $652
2. Comparison of WoolCorp’s current method with activity-based costing:
Raw Wool Wool Yarn
Allocated factory
overhead cost $45,640 $19,560
Activity-Based Costing $17,840 $47,640
3. Calculation of and entering the activity rate for each of the three activities:
Activity Activity Rate
Sorting $6.40 ($25,600/4,000)
Cleaning $6.00 ($38,400/6,400)
Combing $12.00 $1,200/100)
4. Allocation of the costs of sorting, cleaning, and combing to product:
Raw Wool Wool Yarn
Sorting cost $5,120 $20,400
Cleaning cost 11,520 26,880
Combing cost 840 360
Total cost $17,840 $47,640
5. Recommended method of costing:
Activity-based costing, because it recognizes differences in how each product uses factory overhead activities, yielding more accurate product costs.
Explanation:
Key Decisions: product offerings, pricing, and vendors
Problem: method of assigning overhead to products
Products:
(1) raw, clean wool to be used as stuffing or insulation and
(2) wool yarn for use in the textile industry
Requirement: evaluate its costing methods for its raw wool and wool yarn.
Traditional Costing Method : Predetermined overhead rate computed as follows:
Single Plantwide Factory Overhead Rate= (Total Budgeted Factory Overhead) ÷ (Total Budgeted Plantwide Allocation Base) combing machine hours
Data for the production of 550 pounds of either raw wool or wool yarn:
Factory Overhead Type Budgeted Factory Overhead
Sorting $25,600
Cleaning $38,400
Combing $1,200
Total overhead $65,200
Raw Wool Wool Yarn
Hours of combing
machine use required 70 30
Compiled Information:
Type of Cost Activity Base Total Cost Rate
Sorting Hours of sorting $25,600
Cleaning Units of cleaning
machine power $38,400
Combing Hours of combing
machine use $1,200
Raw Wool Wool Yarn Total
Hours of sorting required 800 3,200 4,000
Units of cleaning machine
power required 1,920 4,480 6,400
Hours of combing
machine use required 70 30 100
1.Overhead Rate = Overhead Costs/ Direct Labor Costs
Budget Overhead Rate = 3060,000/ 1700,000= 1.8
Actual Overhead Rate = 3217,500/ 1650,000= 1.895
Dakota Products
Budget for 2017 Actual Results for 2017
Direct material costs $2,250,000 $2,150,000
Direct manufacturing labor costs 1,700,000 1,650,000
Manufacturing overhead costs 3,060,000 3,217,500
2.During March, the job-cost record for Job 626
Direct materials used $55,000
Direct manufacturing labor costs $45,000
Actual Overhead = 1.895 * $45,000= $ 85295.45
Normal Overhead = 1.8 * 45,000= $ 81,000
2.The actual cost of Job 626 =$ 55,000+ $ 45,000+ $ 85295.45= $ 185,295.45
2.The normal cost of Job 626 =$ 55,000+ $ 45,000+ $ 81,000= $181,000
3. Under- or Overallocated Overhead under normal costing=
Budgeted Overhead - Actual Overhead= 3,060,000 - 3,217,500=
157,500 underapplied
There is no under- or overallocated overhead under actual costing because overhead costs actually are at their actual costs. There is no difference between calculated and actual.
4. Normal Costing would give an idea before 2017 and it is easier to make decision prior to changes. Actual results can only be obtained after the process. Managers find it easier to pre plan . So normal costing is adoptable.
WoolCorp
1. Single Plantwide Factory Overhead Rate: $652
2. Comparison of WoolCorp’s current method with activity-based costing:
Raw Wool Wool Yarn
Allocated factory
overhead cost $45,640 $19,560
Activity-Based Costing $17,840 $47,640
3. Calculation of and entering the activity rate for each of the three activities:
Activity Activity Rate
Sorting $6.40 ($25,600/4,000)
Cleaning $6.00 ($38,400/6,400)
Combing $12.00 $1,200/100)
4. Allocation of the costs of sorting, cleaning, and combing to product:
Raw Wool Wool Yarn
Sorting cost $5,120 $20,400
Cleaning cost 11,520 26,880
Combing cost 840 360
Total cost $17,840 $47,640
5. Recommended method of costing:
Activity-based costing, because it recognizes differences in how each product uses factory overhead activities, yielding more accurate product costs.
Explanation:
Key Decisions: product offerings, pricing, and vendors
Problem: method of assigning overhead to products
Products:
(1) raw, clean wool to be used as stuffing or insulation and
(2) wool yarn for use in the textile industry
Requirement: evaluate its costing methods for its raw wool and wool yarn.
Traditional Costing Method : Predetermined overhead rate computed as follows:
Single Plantwide Factory Overhead Rate= (Total Budgeted Factory Overhead) ÷ (Total Budgeted Plantwide Allocation Base) combing machine hours
Data for the production of 550 pounds of either raw wool or wool yarn:
Factory Overhead Type Budgeted Factory Overhead
Sorting $25,600
Cleaning $38,400
Combing $1,200
Total overhead $65,200
Raw Wool Wool Yarn
Hours of combing
machine use required 70 30
Compiled Information:
Type of Cost Activity Base Total Cost Rate
Sorting Hours of sorting $25,600
Cleaning Units of cleaning
machine power $38,400
Combing Hours of combing
machine use $1,200
Raw Wool Wool Yarn Total
Hours of sorting required 800 3,200 4,000
Units of cleaning machine
power required 1,920 4,480 6,400
Hours of combing
machine use required 70 30 100
1.Overhead Rate = Overhead Costs/ Direct Labor Costs
Budget Overhead Rate = 3060,000/ 1700,000= 1.8
Actual Overhead Rate = 3217,500/ 1650,000= 1.895
Dakota Products
Budget for 2017 Actual Results for 2017
Direct material costs $2,250,000 $2,150,000
Direct manufacturing labor costs 1,700,000 1,650,000
Manufacturing overhead costs 3,060,000 3,217,500
2.During March, the job-cost record for Job 626
Direct materials used $55,000
Direct manufacturing labor costs $45,000
Actual Overhead = 1.895 * $45,000= $ 85295.45
Normal Overhead = 1.8 * 45,000= $ 81,000
2.The actual cost of Job 626 =$ 55,000+ $ 45,000+ $ 85295.45= $ 185,295.45
2.The normal cost of Job 626 =$ 55,000+ $ 45,000+ $ 81,000= $181,000
3. Under- or Overallocated Overhead under normal costing=
Budgeted Overhead - Actual Overhead= 3,060,000 - 3,217,500=
157,500 underapplied
There is no under- or overallocated overhead under actual costing because overhead costs actually are at their actual costs. There is no difference between calculated and actual.
4. Normal Costing would give an idea before 2017 and it is easier to make decision prior to changes. Actual results can only be obtained after the process. Managers find it easier to pre plan . So normal costing is adoptable.
A. Particular Direct Indirect Variable Fixed
1 Wages of Assembly Yes No Yes No
2 Deprecation of plant & No Yes No Yes
Machinery
3 Glue & Thread No No Yes No
4 Outbound Shipping Cost No Yes No Yes
5 Raw Material Handling Cost Yes No Yes No
6Salary Of Public Relations No Yes No Yes
manager
7 Production Run Setup Costs Yes No Yes No
8 Plant Utilities Yes No Yes No
9 Electricity cost of retail stores No Yes Yes No
10 Research and development No Yes No Yes
expense
B. Product-Costing
i. Manufacturing Cost Per Machine Hour = Total Manufacturing overhead / Total Machine Hours
Manufacturing Cost Per Machine Hour = 359,520.00 / 21,400.00
Manufacturing Cost Per Machine Hour = 16.80
ii. Particular Amount
Raw Material $6,240
Direct Labor Cost $9,165
$15,405
Manufacturing overhead $13,104
(780 hours* $16.80)
Total Cost of 3900 Hats $28509
Thus, the Cost of One hat = $28509 / 3900 hat = $7.31 per hat
iii. Total Hats made During the Month Of April 3,900
Less: Closing Inventory 1,050
Sold During the month of April 2,850
Cost Of Hats Sold During the month of April
= 2,850 * $7.31
= $20,833.5
Cost of Closing Stock (1,050 hat) = 1,050 hat * $7.31 = 7675.5
 4
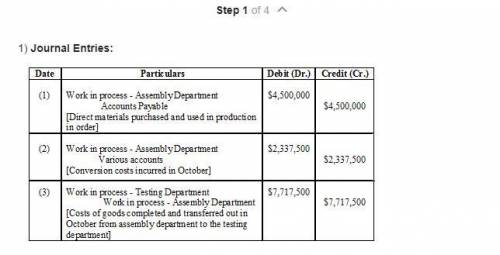
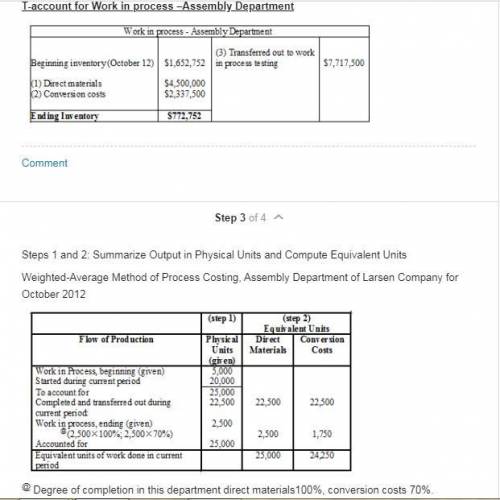
4 Answer for the question:
Larsen company manufactures car seats in its San Antonio plant. Each car seat passes through the Assembly department and the Testing Department. This problem focuses on the Assembly Department. The process-costing system at Larsen Company has a single direct-cost category ( direct materials) and a single indirect-cost category (conversion costs). Direct materials are added at the beginning of the process. Conversion costs are added evenly during the process. When the Assembly Department finishes work on each car seat, it is immediately transferred to Testing.
Larsen Company uses the weighted-average method of process costing. Data for the Assembly Department for October 2009 are:
the physical units are the car seats
Physical Units Direct Materials Conversion Costs
work in process
october 1(a) 5,000 $1,250,000 $402,750
started during
october 2009 20,000
completed during
october 2009 22,500
work in process
october 31(b) 2,500
total costs added
during october 2009 $4,500,000 $2,337,500
a-degree of completion: direct materials ?%: conversion costs, 60%
b-degree of completion: direct materials ?%: conversion costs, 70%
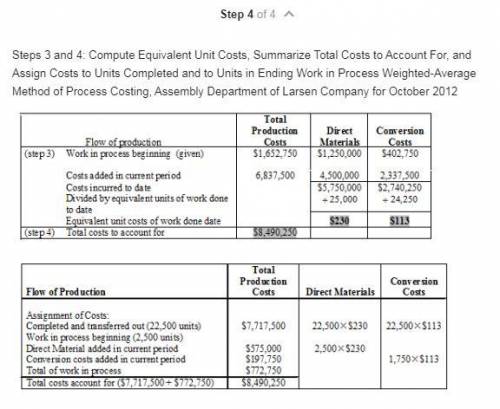
1. For each costs category, compute equivalent units in the Assemly Department. Show physical units in the first column of your schedule.
2. What issues should the manager focus on when reviewing the equivalent units calculation?
3. For each cost category, summarize total assembly department costs for Octoer 2014 and calculate the costs per equivalent unit.
4. Assign costs to units completed and transferred out and to units in ending work in process.
Is given in the attachment.
Explanation:
 1
1 Kindly check attached picture
Explanation:
Required:
1. According to the activity-based costing system, what is the total cost of serving each of the following parties of diners? (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.)
a. A party of four dinners who order three drinks-?
b. A party of two dinners who do not order any drinks-?
c. A party of one dinner who order two drinks-?
2. Convert the total costs you computed in (1) above to costs per diner. In other words, what is the average cost per diner for serving each of the following parties? (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places and final answers to 3 decimal places.)
a. A party of four dinners who order three drinks-?
b. A party of two dinners who do not order any drinks-?
c. A party of one dinner who order two drinks-?
Kindly check attached picture for detailed explanation.

 4
4 Answer for the question:
Larsen company manufactures car seats in its San Antonio plant. Each car seat passes through the Assembly department and the Testing Department. This problem focuses on the Assembly Department. The process-costing system at Larsen Company has a single direct-cost category ( direct materials) and a single indirect-cost category (conversion costs). Direct materials are added at the beginning of the process. Conversion costs are added evenly during the process. When the Assembly Department finishes work on each car seat, it is immediately transferred to Testing.
Larsen Company uses the weighted-average method of process costing. Data for the Assembly Department for October 2009 are:
the physical units are the car seats
Physical Units Direct Materials Conversion Costs
work in process
october 1(a) 5,000 $1,250,000 $402,750
started during
october 2009 20,000
completed during
october 2009 22,500
work in process
october 31(b) 2,500
total costs added
during october 2009 $4,500,000 $2,337,500
a-degree of completion: direct materials ?%: conversion costs, 60%
b-degree of completion: direct materials ?%: conversion costs, 70%
1. For each costs category, compute equivalent units in the Assemly Department. Show physical units in the first column of your schedule.
2. What issues should the manager focus on when reviewing the equivalent units calculation?
3. For each cost category, summarize total assembly department costs for Octoer 2014 and calculate the costs per equivalent unit.
4. Assign costs to units completed and transferred out and to units in ending work in process.
Is given in the attachment.
Explanation:




It will provide an instant answer!
