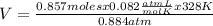1) The compound which can act as a Bronsted-Lowry acid and a Bronsted-Lowry base is definitely water - H2O. Remember that water is amphoteric which means it can either accept protons or donate them, so it is the most proper option among other represented. Here are examples of both base and acid with water : HCl+H20=H30+Cl ; NH3+H2O=NH4+OH
2) The acids in this equilibrium reaction CN– + H2O HCN + OH. Acid species always donate H+ to the species with which they react. In the second option you can see how H2O donates an H+ to CN-. If the reaction gets reversed we will obtain HCN that donates an H+ to OH that shows that it is an acid.
3) The products of self-ionization of water are OH⁻ and H₃O⁺. Self-ionization is an ionization reaction during which H2O deprotonates its hydrogen atoms to become a hydroxide ion -- OH−. After this process OH- protonates another water molecule forming H3O+.
4) The type of solution which is one with a pH of 8 is acidic. Here is a little table that can be a prompt for you if you ever come across such tasks - ph : 7 is neutral. pH lower than 7 are acidic, and pH higher than 7 basic ones.
5) The acid dissociation constant for an acid dissolved in water is equal to the equilibrium constant. I consider this option correct because we can obtan Kw only when dealing with Kb, and we can conclude that the hydrolysis constant of the conujugate base.
6) A 0.12 M solution of an acid that ionizes only slightly in solution would be termed dilute and weak. You can determine it depending on its concentration. Such value as 0.12M usually defined as a dilute solution of a weak acid due to the fact that acid represents its partial ionization which is a direct characteristic of a weak acid.
7) To solve this task we should appeal to Henry's law that says the solubility of a gaz is proportional to its partial pressure. And according to this we can understand that 202kPa is the half of 404kPa which means that the needed solubility must be divided by 2 7.5/2=3.75 g/L and that's all.
8) I think that the most important points which best show how the addition of a solute affects the boiling point, the freezing
point, and the vapor pressure of the solvent are : BOILING: additional attractive forces can only exist between solute and solvent and in order to boil they must be overcome for the solution;we should add KE to overcome the forces. FREEZING : to freeze we have to withdrawn KE as the solute particles are surrounded by solvent molecules. VAPOR : WHen solvent shells are being formed the solute particles reduces the number of solvent particles that have sufficient KE to vaporize.
9)
![[H+][OH-]= Kw = 1.0 * 10^-14](/tpl/images/0287/2817/b9e7e.png)
![[H+]= Kw/ [OH-]= 1.0x 10^-14 / 1 x 10^-11 =1 x 10^-3 mol/L pH = - log [H+]= - log 1 x 10^-3 = 3](/tpl/images/0287/2817/63f2b.png)
Since we got Ph of 3 in a result we can define solution as an acidic one, as I mentioned before.
10) Since the formula of the given acid is HA it undergoes like that : HA<=> H+ + A- .
ka = [H][A] / [HA].
Now we have only [H+] and to go further you need to write electroneutrality equation for the reaction :
[H+] = [OH-] + [A-] (since [H]>>>[OH]), then
[H+] = [A-]
Then mass balance equation :
Ct = 0.5M = [A-] + [HA]
[HA] = 0.5 - [A-] = 0.5 - [H+]
Finally here is what we have done and get :
![ka = [H]^2 / (0.5 - [H+]) ](/tpl/images/0287/2817/777b7.png)
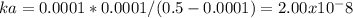
11) The main points that are common for acids : they form Hydrogen ions when dissloved in water, - Ex. Vinegar and Lemon, Ph >7, they have Increased hydrogen ions (H+). The facts about bases : they reduce the concentration of hydgoren ions in a solution which is opposite to asids,- Ex. Antiacid,and Ammonia ,Ph valuse above 7, they form hydrogen (OH-).
- The common points of both acids and bases : Hydrogen ions ,
both not neutral and water based.
 28
28 ![[H+][OH-]= Kw = 1.0 * 10^-14](/tpl/images/0287/2817/b9e7e.png)
![[H+]= Kw/ [OH-]= 1.0x 10^-14 / 1 x 10^-11 =1 x 10^-3 mol/L pH = - log [H+]= - log 1 x 10^-3 = 3](/tpl/images/0287/2817/63f2b.png)
![ka = [H]^2 / (0.5 - [H+]) ](/tpl/images/0287/2817/777b7.png)
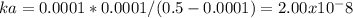
 28
28 ![[H+][OH-]= Kw = 1.0 * 10^-14](/tpl/images/0287/2817/b9e7e.png)
![[H+]= Kw/ [OH-]= 1.0x 10^-14 / 1 x 10^-11 =1 x 10^-3 mol/L pH = - log [H+]= - log 1 x 10^-3 = 3](/tpl/images/0287/2817/63f2b.png)
![ka = [H]^2 / (0.5 - [H+]) ](/tpl/images/0287/2817/777b7.png)
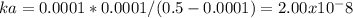

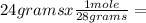 0.857 moles (where 28 g/mole is the molar mass of N₂, that is, the amount of mass that the substance contains in one mole.)
0.857 moles (where 28 g/mole is the molar mass of N₂, that is, the amount of mass that the substance contains in one mole.)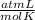
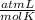 ×328 K
×328 K