 3
3 a) N2 is the limiting reactant
b) 1215.9 grams NH3
c) 2283.6 grams H2
Explanation:
Step 1: Data given
Mass of N2 = 1000 grams
Molar mass N2 = 28 g/mol
Mass of H2 = 2500 grams
Molar mass H2 = 2.02 g/mol
Step 2: The balanced equation
N2(g) +3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
Step 3: Calculate moles N2
Moles N2 = mass N2 / molar mass N2
Moles N2 = 1000 grams / 28.0 g/mol
Moles N2 = 35.7 moles
Step 4: Calculate moles H2
Moles H2 = 2500 grams / 2.02 g/mol
Moles H2 = 1237.6 moles
Step 5: Calculate limiting reactant
For 1 mol N2 we need 3 moles H2 to produce 2 moles NH3
N2 is the limiting reactant. There will be consumed 35.7 moles.
H2 is in excess. There will react 3*35.7 = 107.1 moles
There will remain 1237.6 - 107.1= 1130.5 moles H2
This is 1130.5 * 2.2 = 2283.6 grams H2
Step 6: Calculate moles NH3
For 1 mol N2 we need 3 moles H2 to produce 2 moles NH3
For 35.7 moles N2 we'll have 2*35.7 = 71.4 moles NH3
Step 7: Calculate mass NH3
Mass NH3 = moles NH3 * molar mass NH3
Mass NH3 = 71.4 moles * 17.03 g/mol
Mass NH3 = 1215.9 grams NH3
 3
3 a) N2 is the limiting reactant
b) 1215.9 grams NH3
c) 2283.6 grams H2
Explanation:
Step 1: Data given
Mass of N2 = 1000 grams
Molar mass N2 = 28 g/mol
Mass of H2 = 2500 grams
Molar mass H2 = 2.02 g/mol
Step 2: The balanced equation
N2(g) +3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
Step 3: Calculate moles N2
Moles N2 = mass N2 / molar mass N2
Moles N2 = 1000 grams / 28.0 g/mol
Moles N2 = 35.7 moles
Step 4: Calculate moles H2
Moles H2 = 2500 grams / 2.02 g/mol
Moles H2 = 1237.6 moles
Step 5: Calculate limiting reactant
For 1 mol N2 we need 3 moles H2 to produce 2 moles NH3
N2 is the limiting reactant. There will be consumed 35.7 moles.
H2 is in excess. There will react 3*35.7 = 107.1 moles
There will remain 1237.6 - 107.1= 1130.5 moles H2
This is 1130.5 * 2.2 = 2283.6 grams H2
Step 6: Calculate moles NH3
For 1 mol N2 we need 3 moles H2 to produce 2 moles NH3
For 35.7 moles N2 we'll have 2*35.7 = 71.4 moles NH3
Step 7: Calculate mass NH3
Mass NH3 = moles NH3 * molar mass NH3
Mass NH3 = 71.4 moles * 17.03 g/mol
Mass NH3 = 1215.9 grams NH3
Mass of Hydrogen gas required to react : 0.936 g
Further explanationReaction on Nitrogen gas and Hydrogen gas to produce Ammonia gas
N₂ (g) + 3 H₂ (g) ⇒ 2 NH₃ (g)
Conditions at T 0 ° C and P 1 atm are stated by STP (Standard Temperature and Pressure). At STP, Vm is 22.4 liters / mol
so mol Nitrogen for 3.5 L at STP :
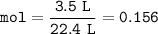
From the equation, mol ratio of N₂ : H₂ = 1 : 3, so mol H₂ :
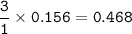
then mass of Hydrogen(MW= 2 g/mol) :


Answer:
AStep-by-step explanation:
The input force is 50 N. But it will not create not any change. No mechanical advantage is observed.

 1
1 Answer:
52.6 gramStep-by-step explanation:
It is clear by the equation 2(27+3×35.5)= 267 gm of AlCl3 reacts with 6× 80 = 480 gm of Br2 . So 29.2 gm reacts = 480× 29.2/267= 52.6 gm
Calcium (Ca)(On the periodic table, ionization energy increases as you go up and to the right of the periodic table)
Answer:
Taking into accoun the ideal gas law, The volume of a container that contains 24.0 grams of N2 gas at 328K and 0.884 atm is 26.07 L.
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas that is considered to be composed of point particles that move randomly and do not interact with each other. Gases in general are ideal when they are at high temperatures and low pressures.
The pressure, P, the temperature, T, and the volume, V, of an ideal gas, are related by a simple formula called the ideal gas law:
P×V = n×R×T
where P is the gas pressure, V is the volume that occupies, T is its temperature, R is the ideal gas constant, and n is the number of moles of the gas. The universal constant of ideal gases R has the same value for all gaseous substances.
Explanation:
In this case, you know:
P= 0.884 atm
V= ?
n= 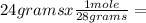 0.857 moles (where 28 g/mole is the molar mass of N₂, that is, the amount of mass that the substance contains in one mole.)
0.857 moles (where 28 g/mole is the molar mass of N₂, that is, the amount of mass that the substance contains in one mole.)
R=0.082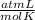
T= 328 K
Replacing in the ideal gas law:
0.884 atm×V= 0.857 moles× 0.082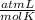 ×328 K
×328 K
Solving:
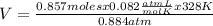
V= 26.07 L
The volume of a container that contains 24.0 grams of N2 gas at 328K and 0.884 atm is 26.07 L.

It will provide an instant answer!
