 19
19 C. 2.0 x 10⁻³
Explanation:
The average rate of a reaction is the rate of change of the concentration of the reactants (or products) with time.
The average rate of the reaction = - (ΔC)/(Δt).
∵ The concentration of the reactants changes from 1.8 M to 0.6M for 580 s.
∴ The average rate of the reaction over the first 580 seconds
= - (ΔC)/(Δt) = - [(0.6M) - (1.8 M)]/[(580.0 s) - (0.0 s)] = 2.0 x 10⁻³ M.s⁻¹.
So C. 2.0 x 10⁻³ is the right answer
 33
33 2.0 x 10⁻³ M/s.
Explanation:
The rate of the reaction is the change of the concentration of the reactants or the products with time.The rate of the reaction = - Δ[reactants]/Δt = - [(0.6 M - 1.8 M)]/(580 s - 0 s) = 2.069 x 10⁻³ M/s.
 6
6 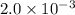
Solution:
Average rate is the ratio of concentration change to the time taken for the change
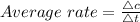
The concentration of the reactants changes 1.8 M to 0.6 M
here, the time interval given is 0 to 580 sec
Therefore,
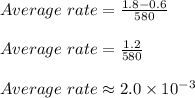
Thus option C is correct
 6
6 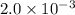
Solution:
Average rate is the ratio of concentration change to the time taken for the change
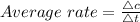
The concentration of the reactants changes 1.8 M to 0.6 M
here, the time interval given is 0 to 580 sec
Therefore,
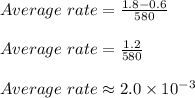
Thus option C is correct
Explanation:
average rate is defined as the ratio of concentration change to the time taken for the change.it does not depend on the way in which the concentration change.it depends only on the initial and final concentrations in the given time in which we have to find the average rate.here, the time interval given is 0 to 580 sec
the concentration change (c) = 1.8 - 0.6 = 1.2 M
time (t) = 580 sec
average rate (r) = 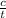 =
= 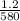 ≅
≅ 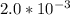
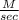
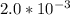
Explanation:
average rate is defined as the ratio of concentration change to the time taken for the change.it does not depend on the way in which the concentration change.it depends only on the initial and final concentrations in the given time in which we have to find the average rate.here, the time interval given is 0 to 580 sec
the concentration change (c) = 1.8 - 0.6 = 1.2 M
time (t) = 580 sec
average rate (r) = 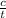 =
= 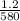 ≅
≅ 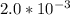
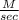
 10
10 The concentration of the reactants decreases.
Explanation: Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
k= rate constant
x = order with respect to
y = order with respect to
Thus as the concentration of reactants decrease, the rate of the reaction also decrease and thus the rate of formation of products decrease.
 10
10 The concentration of the reactants decreases.
Explanation: Rate law says that rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants each raised to a stoichiometric coefficient determined experimentally called as order.
k= rate constant
x = order with respect to
y = order with respect to
Thus as the concentration of reactants decrease, the rate of the reaction also decrease and thus the rate of formation of products decrease.
Answer:
AStep-by-step explanation:
The input force is 50 N. But it will not create not any change. No mechanical advantage is observed.

It will provide an instant answer!
