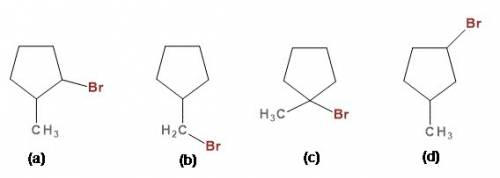
We have to know the structure of the isomer of C₆H₁₁Br which contains 5-membered ring and is least reactive in an SN¹ reaction.
The structure is: isomer (a) shown in figure where methyl group and Br atom connected to the adjacent carbons in the ring.
There are four isomers possible with molecular formula C₆H₁₁Br. Those are shown in figure as (a), (b), (c), (d).
SN¹ reaction takes place through carbocation intermediate formation. If carbocation is more stable, SN¹ reaction will be more faster and if carbocation is not stable, SN¹ reaction will be slower.
The stability of carbocation depends on number of α-H atoms. If the number of α-H atom is more, hyperconjugation in the carbocation will be more; as a consequence, SN¹ reaction rate will be faster.
On the other hand, if the number of α-H atom is less, hyperconjugation in the carbocation will be less; as a consequence, SN¹ reaction rate will be slow.
The carbocation of isomer (a) contains α-H atom= 3, all other isomers contain minimum 4 α-H atoms.