The mole fraction of the solvent in a solution that contains 2.51 g glycerol dissolved in 21.10 mL ethanol is 0.93
Explanation:
Given : Volume of ethanol (solvent) = 21.10 ml
density of ethanol (solvent)= 0.789 g/ml
Mass of glycerol (solute) = 2.51 g
Mole fraction of a component is the ratio of moles of that component to the total moles present.
mole fraction of ethanol (solvent) = 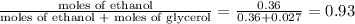
The mole fraction of the solvent in a solution that contains 2.51 g glycerol dissolved in 21.10 mL ethanol is 0.93