Answer:
Taking into accoun the ideal gas law, The volume of a container that contains 24.0 grams of N2 gas at 328K and 0.884 atm is 26.07 L.
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas that is considered to be composed of point particles that move randomly and do not interact with each other. Gases in general are ideal when they are at high temperatures and low pressures.
The pressure, P, the temperature, T, and the volume, V, of an ideal gas, are related by a simple formula called the ideal gas law:
P×V = n×R×T
where P is the gas pressure, V is the volume that occupies, T is its temperature, R is the ideal gas constant, and n is the number of moles of the gas. The universal constant of ideal gases R has the same value for all gaseous substances.
Explanation:
In this case, you know:
P= 0.884 atm
V= ?
n= 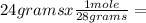 0.857 moles (where 28 g/mole is the molar mass of N₂, that is, the amount of mass that the substance contains in one mole.)
0.857 moles (where 28 g/mole is the molar mass of N₂, that is, the amount of mass that the substance contains in one mole.)
R=0.082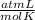
T= 328 K
Replacing in the ideal gas law:
0.884 atm×V= 0.857 moles× 0.082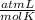 ×328 K
×328 K
Solving:
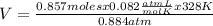
V= 26.07 L
The volume of a container that contains 24.0 grams of N2 gas at 328K and 0.884 atm is 26.07 L.