The sun is so far away that it practically shines equally at the equator and the poles. But why is the equator very hot and the poles very cold?
There are several factors that influence the amount of sunshine received at various places on the earth.
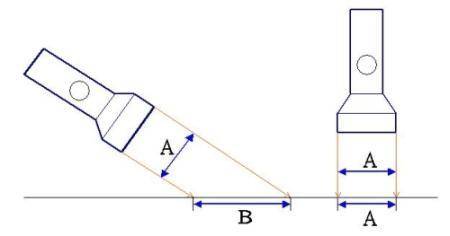
The major factor is that while the sun is overhead at the equator, it is at a rather slant angle at the poles. This effect can be demonstrated using a torch, which can be taken as the sun. See Figure 1. What really counts is the amount of sunshine that falls on a given area. At the equator, the area A receives the same amount of sunshine as another area B at a higher latitude. Since, from Figure 1, B is clearly greater than A, the amount of sunshine that falls on a unit area (for instance a square metre) at area B is less than that at area A. In other words, for the same area of 1 square metre, the amount of sunshine received is greater at A than at B.The sun is so far away that it practically shines equally at the equator and the poles. But why is the equator very hot and the poles very cold?
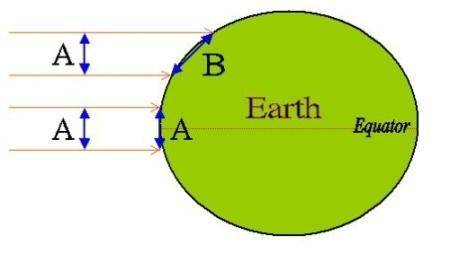
Explanation: Figure 2: Rays from the sun to the earth. The area lit by the sun's ray is greater at A than at B. So, the solar energy falling on a unit area is greater at the tropics than at higher latitudes.
The other factors, which are less important, include:-
a) Absorption and scattering of sunshine when passing through the atmosphere - the amount of absorption and scattering depends on the nature and concentration of air molecules and small particles in the atmosphere. All things being equal, at higher latitudes the sun's path is longer. Naturally, there are more air molecules and particles along the way, resulting in greater absorption and scattering. Hence less solar energy reaches these places.
b) Reflection by the earth's surface. As the sun's ray reaches the earth, some of the energy is reflected back and does not warm up the place. The amount of reflection depends on the nature of the surface. Snow is an extreme in terms of reflection, since as much as 75 to 95% of the incoming sunshine is bounced back - not much help for the already cold weather in snow-covered areas. However, with an overall decreasing trend in snow cover in recent years due to climate change, more and more solar energy gets absorbed. A very likely consequence is still warmer conditions and less snow cover, further aggravating the equilibri