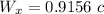
Explanation:
given,
velocity of particle 1 = 0.741 c to left
velocity of second particle = 0.543 c to right
relative velocity between the particle = ?
for the relative velocity calculation we have formula
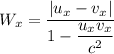
u_x = 0.543 c
v_x = - 0.741 c
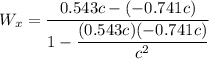
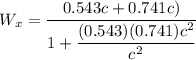
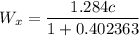
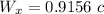
Relative velocity of the particle is 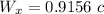
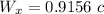
Explanation:
given,
velocity of particle 1 = 0.741 c to left
velocity of second particle = 0.543 c to right
relative velocity between the particle = ?
for the relative velocity calculation we have formula
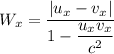
u_x = 0.543 c
v_x = - 0.741 c
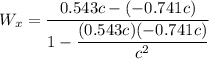
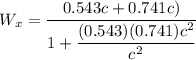
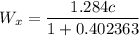
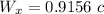
Relative velocity of the particle is 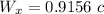
 6
6 (a) The velocity at time t, is 3t² - 16t + 28.
(b) The velocity after 1 second is 15 ft/s.
(c) The time when the particle is at rest does not exist.
(d) the particle is always moving in positive direction.
(e) The total distance traveled during first 6 seconds is 96 feet.
The given equation of motion;
f(t) = t³ - 8t² + 28t
(a) The velocity at time t, is calculated as follows;
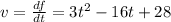
(b) The velocity after 1 second is calculated as follows;
v = 3(1)² - 16(1) + 28
v = 15 ft/s
(c) When the particles is at rest, the velocity is zero;
3t² -16t + 28 = 0
solve the quadratic equation using formula method;
a = 3, b = -16, c = 28
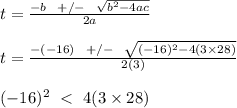
Thus, the time when the particle is at rest does not exist.
(d) The time of motion of the is greater than or equal to zero.
t ≥ 0
when t = 0
f(0) = (0)³ - 8(0)² + 28(0)
f(0) = 0 - 0 + 0
f(0) = 0
when t = 1
f(1) = (1)³ - 8(1) + 28(1)
f(1) = 1 - 8 + 28
f(1) = 21 feet
Thus, the particle started from zero origin and moves towards positive direction.
(e) The total distance traveled during first 6 seconds is calculated as follows;
f(6) = (6)³ - 8(6)² + 28(6)
f(6) = 96 feet.
Learn more here:link
a) 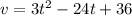 is the velocity of the particle at any time t.
is the velocity of the particle at any time t.
b) 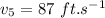
c) The particle is at rest at time t=2 seconds.
d) At time t=2 seconds the particle posses positive velocity being at positive direction.
e) 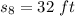
Explanation:
Given:
The function of displacement dependent on time,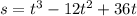 .......(1)
.......(1)
a)
Now as we know that velocity is the time derivative of the displacement:
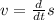

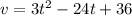 ..........................(2)
..........................(2)
b)
Now the velocity after 5 seconds:
put t=5 in eq. (2)
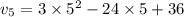
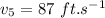
c)
When the particle is at rest it has zero velocity.
Now velocity at time t=6 s:
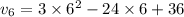
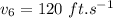
Now velocity at time t=2 s:
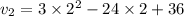
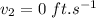
The particle is at rest at time t=2 seconds.
d)
Put the value t=2 sec. in eq. (1):
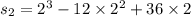
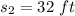
At time t=2 seconds the particle posses positive velocity being at positive direction.
e)
Distance travelled during the first 8 seconds:
put t=8 in eq. (1)
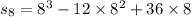
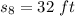
 6
6 (a) The velocity at time t, is 3t² - 16t + 28.
(b) The velocity after 1 second is 15 ft/s.
(c) The time when the particle is at rest does not exist.
(d) the particle is always moving in positive direction.
(e) The total distance traveled during first 6 seconds is 96 feet.
The given equation of motion;
f(t) = t³ - 8t² + 28t
(a) The velocity at time t, is calculated as follows;
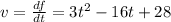
(b) The velocity after 1 second is calculated as follows;
v = 3(1)² - 16(1) + 28
v = 15 ft/s
(c) When the particles is at rest, the velocity is zero;
3t² -16t + 28 = 0
solve the quadratic equation using formula method;
a = 3, b = -16, c = 28
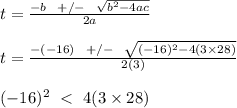
Thus, the time when the particle is at rest does not exist.
(d) The time of motion of the is greater than or equal to zero.
t ≥ 0
when t = 0
f(0) = (0)³ - 8(0)² + 28(0)
f(0) = 0 - 0 + 0
f(0) = 0
when t = 1
f(1) = (1)³ - 8(1) + 28(1)
f(1) = 1 - 8 + 28
f(1) = 21 feet
Thus, the particle started from zero origin and moves towards positive direction.
(e) The total distance traveled during first 6 seconds is calculated as follows;
f(6) = (6)³ - 8(6)² + 28(6)
f(6) = 96 feet.
Learn more here:link
a) 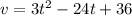 is the velocity of the particle at any time t.
is the velocity of the particle at any time t.
b) 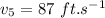
c) The particle is at rest at time t=2 seconds.
d) At time t=2 seconds the particle posses positive velocity being at positive direction.
e) 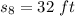
Explanation:
Given:
The function of displacement dependent on time,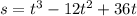 .......(1)
.......(1)
a)
Now as we know that velocity is the time derivative of the displacement:
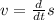

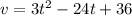 ..........................(2)
..........................(2)
b)
Now the velocity after 5 seconds:
put t=5 in eq. (2)
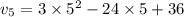
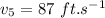
c)
When the particle is at rest it has zero velocity.
Now velocity at time t=6 s:
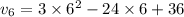
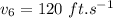
Now velocity at time t=2 s:
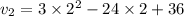
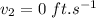
The particle is at rest at time t=2 seconds.
d)
Put the value t=2 sec. in eq. (1):
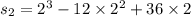
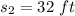
At time t=2 seconds the particle posses positive velocity being at positive direction.
e)
Distance travelled during the first 8 seconds:
put t=8 in eq. (1)
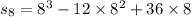
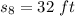
Explanation:
Given
displacement is given by
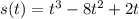
so velocity is given by
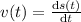
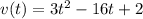
(b)velocity after 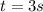
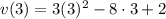
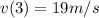
(c)Particle is at rest
when its velocity will become zero
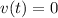
i.e. 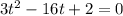
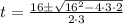
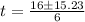
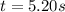
 1
1 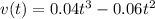
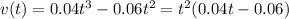
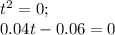
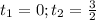
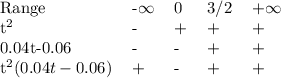
 and t>3/2.
and t>3/2.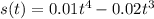
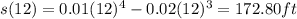
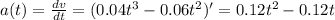
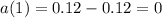
Explanation:
Given
displacement is given by
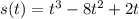
so velocity is given by
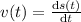
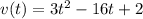
(b)velocity after 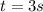
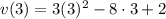
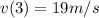
(c)Particle is at rest
when its velocity will become zero
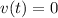
i.e. 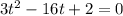
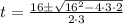
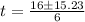
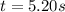
 1
1 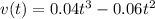
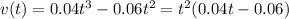
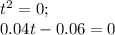
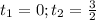
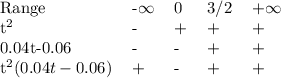
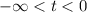 and t>3/2.
and t>3/2.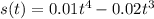

It will provide an instant answer!
