This question is incomplete, the complete question is;
A 1800 kg hybrid vehicle operates on ethanol and is equipped with a multipurpose motorgenerator-flywheel. When the vehicle slows or stops, 50% of the kinetic energy is recovered as electrical energy in the battery. When the IC engine is used to recharge the battery, there is a 25% efficiency of converting chemical energy in the fuel to electrical energy stored in the battery. The vehicle slows from 70 miles per hour to 20 miles per hour. Calculate: (A) Electrical energy recovered in the battery in [kJ] (B) Mass of fuel needed to store same amount of energy in the battery in [kg]
a) Electrical energy recovered in the battery is 404.6895 kJ
b) Mass of fuel needed to store same amount of energy in the battery is 0.0606 kg
Explanation:
Given that;
Initial speed of the vehicle V = 70 miles per hour = 31.293 m/s
Final speed of the vehicle u = 20 miles per hour = 8.941 m/s
mass of vehicle m = 1800 kg
Noe, change in kinetic energy of the vehicle will be;
we substitute
= 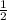 × 1800( (31.293)² - (8.941)² )
× 1800( (31.293)² - (8.941)² )
= 900( 979.2518 - 79.9414)
= 900 × 899.3104
= 809379.36 J
now, Electrical energy recovered in the battery when the vehicle slows will be;
Therefore, Electrical energy recovered in the battery is 404.6895 kJ
b)
For this electrical energy to be obtained from fuel, the chemical energy required will be;
Heat energy released per mass of ethanol combustion
(Lower heating value of ethanol) is 26.7kJ/g
Now, the mass of fuel needed to generate 1618.758 kJ will be;
Therefore, Mass of fuel needed to store same amount of energy in the battery is 0.0606 kg