 1
1 When the mass of an object increases, its gravitational pull also increases.
What is the big bang?The big bang describes the formation of the universe from an initial explosion according to physicists.
We know that the gravitational force between objects is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to their distances apart.
Hence, the two statements which are scientific facts that explain this phenomenon described are;
Gravitation between two objects increases when the distance between them decreases.When the mass of an object increases, its gravitational pull also increases.Learn more about gravitational force:link
 72
72  3
3 C and E
Explanation:
The answer is:
Gravitation between two objects increases when the distance between them decreases.When the mass of an object increases, its gravitational pull also increases.And it is all explained with one formula: the Newton's Universal Law of Gravity:
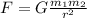
Where F is the gravitational force or pull, G is the gravitational constant, m means mass and r is the distance between the two objects.
In the moments after the big bang, the atoms in gas clouds were gathering together forming what we know now as galaxies, meanwhile as expansion was continuing, the distance between atoms in other regions of the universe was increasing. If we look at Newton's law, the square of the distance is inversely proportional to the Gravitational Force, so, as the distance increases, the Gravitational Force decreases.
On the other matter, now with gravitational force increasing in gas clouds, the cumulative mass of atom groups inside said gas clouds was increasing, while atoms in other part of the universe, being apart, suffered no cumulative increase of mass. Again, looking at the formula, if either 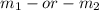 increases, them being directly proportional to F, if the mass increases the gravitational pull also increases.
increases, them being directly proportional to F, if the mass increases the gravitational pull also increases.
 72
72  1
1 When the mass of an object increases, its gravitational pull also increases.
What is the big bang?The big bang describes the formation of the universe from an initial explosion according to physicists.
We know that the gravitational force between objects is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to their distances apart.
Hence, the two statements which are scientific facts that explain this phenomenon described are;
Gravitation between two objects increases when the distance between them decreases.When the mass of an object increases, its gravitational pull also increases.Learn more about gravitational force:link
 3
3 C and E
Explanation:
The answer is:
Gravitation between two objects increases when the distance between them decreases.When the mass of an object increases, its gravitational pull also increases.And it is all explained with one formula: the Newton's Universal Law of Gravity:
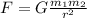
Where F is the gravitational force or pull, G is the gravitational constant, m means mass and r is the distance between the two objects.
In the moments after the big bang, the atoms in gas clouds were gathering together forming what we know now as galaxies, meanwhile as expansion was continuing, the distance between atoms in other regions of the universe was increasing. If we look at Newton's law, the square of the distance is inversely proportional to the Gravitational Force, so, as the distance increases, the Gravitational Force decreases.
On the other matter, now with gravitational force increasing in gas clouds, the cumulative mass of atom groups inside said gas clouds was increasing, while atoms in other part of the universe, being apart, suffered no cumulative increase of mass. Again, looking at the formula, if either 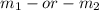 increases, them being directly proportional to F, if the mass increases the gravitational pull also increases.
increases, them being directly proportional to F, if the mass increases the gravitational pull also increases.
 6
6  58
58 After the big bang, atoms in gas clouds experienced a greater gravitational pull to each other than atoms in other regions of the universe. The two statements that explain this phenomenon are statements C and E
C: Gravitation between two objects increases when the distance between them decreases. As gravity is inversely proportional to the square of the separation distance between the two objects, this simplifies that more separation distance will result in weaker gravitational forces and vice versa.
E: When the mass of an object increases, its gravitational pull also increases. The gravitational force increases as the size of an object increases.
 24
24 the answer is below
Explanation: The independent variable is the experimental factor which is manipulated and the variable whose effects are being studied. The dependent variable is a variable that could change due to the independent variable. The independent variable is the different ways that Jennifer treats her puppies in order to bring them closer to what she wants in the agility competition. The dependent variable is how they puppies perform each day.
Behavioral shaping is a conditioning procedure where the reinforcers guide behavior toward closer and closer approximations of a desired behavior. Jennifer guided Sasha closer and closer to completing a behavior correctly, thus utilizing shaping in order to bring the puppy closer to what she wanted.
 2
2 Answer Part A:
1. There is a significant negative relationship between anxiety and academic performance, described as:
a. Subjects with lower anxiety scores have higher current GPAs, or;
b. Subjects who have lower current GPAs have higher anxiety scores.
Explanation:
We can tell that the two variables (anxiety and academic performance) have a negative relationship from its correlation coefficient (-.64). The negative sign shows the relationship, while the statistical significance (p < .01 or p < .05) shows whether there is a relationship or not.
Remember, the power of the correlation (as represented by the number 0.64) does not tell you whether a relationship actually happens or not. It can, however tell the strength of a relationship. A .64 is usually described as moderate to strong, depending on which reference you are using.
Also remember that this is not causation - we do not know which variable causes changes at the other. This is why it is possible to describe the relationship with either option (A) or (B). It is preferable to use a neutral sounding one such as the one stated above: By only saying that there is a negative relationship between the two variables.
2. There is no relationship between hours sleeping per night and academic performance.
Explanation:
A correlation coefficient of 0.00 means that there is no relationship between two variables. The closer a correlation coefficient to 0, the less likely do the variables have a relationship with one another.
Answer Part B:
1. It contributes to the interpretation of the findings by discussing whether:
(1) The measurement used is appropriate for the research conducted,
(2) There are any limitations from the current method of measurement.
Explanation:
The operational definitions in the study are not explicitly stated, but we can come to our own conclusions from the description of the study. They are:
Academic performance is the current GPA as reported by the research subjects.
Anxiety is the anxiety score summed from the research subjects' responses to the anxiety scale.
Interpretation is usually done during the discussion part of a research journal, after the statistical results have been reported. Discussing operational definitions would help determine whether the right measurement is used. Is the method free of biases? For example, Dr. Aguilera used a 5-point scale to measure the student's anxiety levels; there is a possibility of central tendency bias occurring.
2. Cohort effects may contribute to a possible bias over the result of the research. The variations in both anxiety levels and GPA may not be due to each other's influences, but perhaps instead caused by other age-related experience variables such as social media use.
Explanation:
Cohort effects are defined as a condition shared with same-aged groups of people which affected the result of the research. It is a form of bias, when it is not controlled. Dr. Aguilera's study is at risk of being affected with this since her research subjects are all university students.
In the study, we saw that Dr. Aguilera measured social media use, however, she did not seem to control this variable. It is possible that the variation in anxiety is moderated by social media, which then affects the subjects' GPA.

It will provide an instant answer!
