The empirical and molecular formula of the compound is 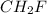 and
and 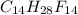 respectively
respectively
Explanation:
We are given:
Mass of 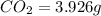
For calculating the mass of carbon:
In 44 g of carbon dioxide, 12 g of carbon is contained.
So, in 3.926 g of carbon dioxide, 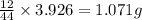 of carbon will be contained.
of carbon will be contained.
To calculate the percentage composition of element in sample, we use the equation:
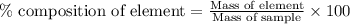 ......(1)
......(1)
For Carbon:
Mass of carbon = 1.071 g
Mass of sample = 2.50 g
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
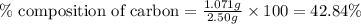
For Fluorine:
Mass of fluorine = 2.54 g
Mass of sample = 5.00 g
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
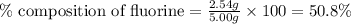
Percent composition of hydrogen = [100 - 42.84 - 50.8] % = 6.36 %
We are given:
Percentage of C = 42.84 %
Percentage of F = 50.8 %
Percentage of H = 6.36 %
Let the mass of compound be 100 g. So, percentages given are taken as mass.
Mass of C = 42.84 g
Mass of F = 50.8 g
Mass of H = 6.36 g
To formulate the empirical formula, we need to follow some steps:
Step 1: Converting the given masses into moles.
Moles of Carbon =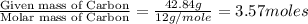
Moles of Hydrogen = 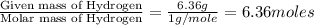
Moles of Fluorine = 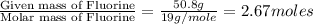
Step 2: Calculating the mole ratio of the given elements.
For the mole ratio, we divide each value of the moles by the smallest number of moles calculated which is 2.67 moles.
For Carbon = 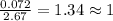
For Hydrogen = 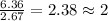
For Fluorine = 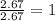
Step 3: Taking the mole ratio as their subscripts.
The ratio of C : H : F = 1 : 2 : 1
The empirical formula for the given compound is 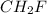
For determining the molecular formula, we need to determine the valency which is multiplied by each element to get the molecular formula.
The equation used to calculate the valency is:
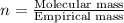
We are given:
Mass of molecular formula = 448.4 g/mol
Mass of empirical formula = ![12+(2\times 1)+19]=33g/mol](/tpl/images/0516/0009/ccdc5.png)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
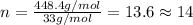
Multiplying this valency by the subscript of every element of empirical formula, we get:
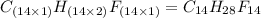
Hence, the empirical and molecular formula of the compound is 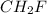 and
and 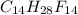 respectively
respectively