sec A= 1.01 and cot B =8.25
Step-by-step explanation:
Given :
sec A and cotB if a =8 and b=7
Now,
=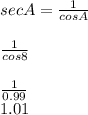
and
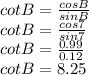
Therefore, answer will be sec A= 1.01 and cot B =8.25
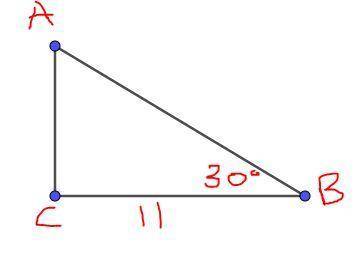
1. The given triangle ABC, has a right angle at C, BC=11, and 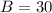
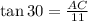
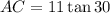
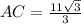
Ans: A
2. The reference angle is the angle the terminal side makes with x-axis.
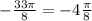
This implies that, 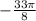 has a reference angle of
has a reference angle of 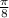 .
.
Ans: C
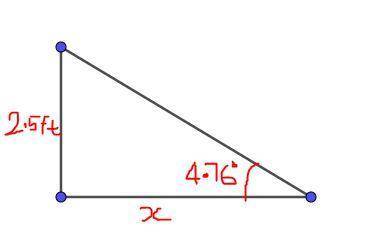
3. Let x be the shortest distance the ramp can span.
From the diagram; 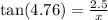
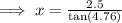
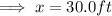
Ans:B
4. Use the Pythagorean identity: 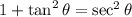 .
.
If 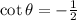 ,then
,then 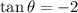
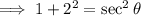
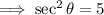
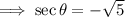 , In QII, the secant ratio is negative.
, In QII, the secant ratio is negative.
Ans:C
5. We have 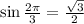
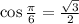
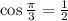
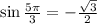
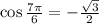
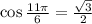
Ans:A and D
6. The given function that is equivalent to 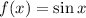 is
is 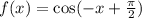 .
.
When we reflect the graph of 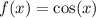 in the y-axis and shift it to the left by
in the y-axis and shift it to the left by 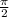 units, it coincides with graph of
units, it coincides with graph of 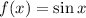 .
.
Ans:C
7. The function 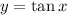 is a one-to-one function on the interval
is a one-to-one function on the interval ![[-\frac{\pi}{2},\frac{\pi}{2}]](/tpl/images/0029/3850/8b799.png)
When we restrict the domain of 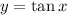 on
on ![[-\frac{\pi}{2},\frac{\pi}{2}]](/tpl/images/0029/3850/8b799.png) it becomes an invertible function.
it becomes an invertible function.
Ans: C
8. The given function is 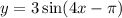
The horizontal shift is given by 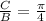
The direction of the shift is to the right.
Ans:D
9. 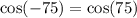 by the symmetric property of even functions.
by the symmetric property of even functions.
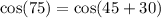
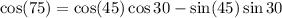
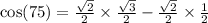
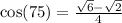
Ans: B
10. Recall the cosine rule: 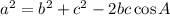
Let the angle measure opposite to the longest side be A, then a=19,b=17, and c=15.
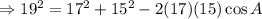
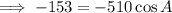
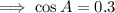
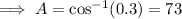
Ans:B
11. We want to solve 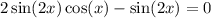 on the interval;
on the interval;
![[-\frac{\pi}{2},\frac{\pi}{2}]](/tpl/images/0029/3850/8b799.png)
Factor: 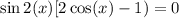
Either 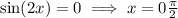
Or 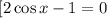 This means that
This means that 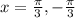
Therefore required solution is 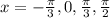
Ans:D
12. Use the relation: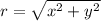 and
and 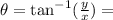
The given rectangular coordinate is (1,-2)
This implies that: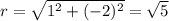
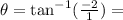 This means
This means 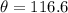 or
or 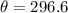
The polar forms are: 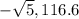 and
and 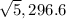
Ans: B and C
13. The polar equation that represents an ellipse is
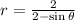 .
.
When written in standard form; 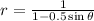 .
.
The eccentricity is 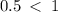 .
.
Therefore the 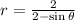 is an ellipse.
is an ellipse.
Ans: B
14. The DeMoivre’s Theorem states that;
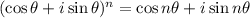
This implies that:
![[2(\cos \frac{\pi}{9}+i\sin \frac{\pi}{9})]^3=2^3\cos 3\times \frac{\pi}{9}+i\sin 3\times \frac{\pi}{9})](/tpl/images/0029/3850/de0fb.png)
![[2(\cos \frac{\pi}{9}+i\sin \frac{\pi}{9})]^3=8(frac{2}{2})+i8(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2})=4+4\sqrt{3}i](/tpl/images/0029/3850/dad44.png)
Ans: A
15. Let the initial point be (x,y), Then 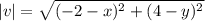 .
.
If x=-8, and y=-4.
Then, 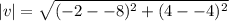 .
.
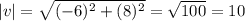 .
.
Ans: B
16. We find the dot product to see if it is zero.
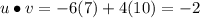
Since the dot product is not zero the vectors are not orthogonal
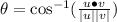
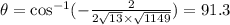
Ans:B
17. Given v=5i+4j, w=2i-3j.
u=v+w
Add corresponding components
This implies u=(5i+4j)+(2i-3j)
u=(5i+2i+4j-3j)
u=7i+j
Ans:B
See attachment.
 13
13  13
13 1. C. 1 + cot²θ = cos²θ
D. 1 - sec²θ = tan²θ
2. D. 0
3. C. Any square is a rectangle
4. C. Parallelogram
5. B. 30 m
6. A. cos(-890°) is Negative
Sin(-890°) is negative
7. A. 100·√3 m
8. 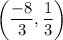
9. First option, A. 68 unit
10. A. 150
Step-by-step explanation:
1. C. 1 + cot²θ = cos²θ
The correct identity is given as follows;
1 + cot²θ = csc²θ
Also
D. 1 - sec²θ = tan²θ
The correct identity is given as follows;
1 - sec²θ = -tan²θ
2. cot(-8550)
We convert -8550 to degrees by dividing by 360 and multiplying the remaining fraction by 360 as follows;
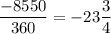
Therefore, -8550 ≅ -3/4×360 = -270
-270 ≅ 360 - 270 = 90°
Therefore, cot(-8550) = cot(90) = 1/(tan(90)) = 1/∞ = 0
Therefore, the correct option is the option D. 0
3. The correct option is any square is a rectangle as a square (a rectangle with all sides equal) is a subset of the set of rectangles
The correct option is C. Any square is a rectangle.
4. Where the diagonals bisect each other, we have a shape where the two opposite triangle areas across the bisector are equal
Therefore, the quadrilateral is necessarily a C. Parallelogram
5. Where by the angle of depression = 45°
Therefore, the angle of elevation = 45° (Alternate angles)
The height of the building = 30 m
Therefore, tan(45°) = (30 m)/(Distance of point A from the building) = 1
∴ The distance of point A from the building = 30 m
The correct option is therefore;
B. 30 m
6. A. -890° = 190° which is in the second quadrant
Therefore, cos(190°) = Negative
B. -1200° = -120° = 240 which is in the third quadrant
Hence, tan(-1200) = tan(240) is positive
C. Sin(1200) = Sin(120) which is in the second quadrant
Hence, sin(1200) is positive
D. Sin(-890°) = Sin(190°) which is in the third quadrant
Hence, sin(-890) is negative
7. The distance from the wall where the measurement is taken = 100/(tan(30)) = 100·√3 = 173.21 m
The total height of the antenna from the ground = 173.21 × tan(45) = 100·√3 m
The total height of the antenna from the ground is 100·√3 m
The correct option is therefore;
A. 100·√3 m
8. The coordinates of the point of intersection of the medians is given by the relation;
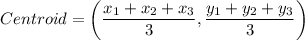
Where:
x₁, y₁ x₂, y₂, x₃, y₃ are the coordinates of the vertices
We therefore have;
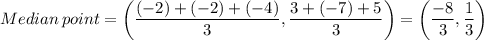
9. The perimeter of the rhombus = 4×√(First diagonal)/2)
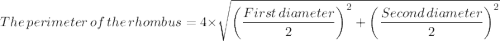
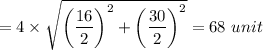
The correct option is A. 68 unit
10. The exterior angle of a regular polygon > 180°, therefore, the correct option is A. 150
1. C. 1 + cot²θ = cos²θ
D. 1 - sec²θ = tan²θ
2. D. 0
3. C. Any square is a rectangle
4. C. Parallelogram
5. B. 30 m
6. A. cos(-890°) is Negative
Sin(-890°) is negative
7. A. 100·√3 m
8. 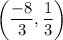
9. First option, A. 68 unit
10. A. 150
Step-by-step explanation:
1. C. 1 + cot²θ = cos²θ
The correct identity is given as follows;
1 + cot²θ = csc²θ
Also
D. 1 - sec²θ = tan²θ
The correct identity is given as follows;
1 - sec²θ = -tan²θ
2. cot(-8550)
We convert -8550 to degrees by dividing by 360 and multiplying the remaining fraction by 360 as follows;
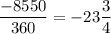
Therefore, -8550 ≅ -3/4×360 = -270
-270 ≅ 360 - 270 = 90°
Therefore, cot(-8550) = cot(90) = 1/(tan(90)) = 1/∞ = 0
Therefore, the correct option is the option D. 0
3. The correct option is any square is a rectangle as a square (a rectangle with all sides equal) is a subset of the set of rectangles
The correct option is C. Any square is a rectangle.
4. Where the diagonals bisect each other, we have a shape where the two opposite triangle areas across the bisector are equal
Therefore, the quadrilateral is necessarily a C. Parallelogram
5. Where by the angle of depression = 45°
Therefore, the angle of elevation = 45° (Alternate angles)
The height of the building = 30 m
Therefore, tan(45°) = (30 m)/(Distance of point A from the building) = 1
∴ The distance of point A from the building = 30 m
The correct option is therefore;
B. 30 m
6. A. -890° = 190° which is in the second quadrant
Therefore, cos(190°) = Negative
B. -1200° = -120° = 240 which is in the third quadrant
Hence, tan(-1200) = tan(240) is positive
C. Sin(1200) = Sin(120) which is in the second quadrant
Hence, sin(1200) is positive
D. Sin(-890°) = Sin(190°) which is in the third quadrant
Hence, sin(-890) is negative
7. The distance from the wall where the measurement is taken = 100/(tan(30)) = 100·√3 = 173.21 m
The total height of the antenna from the ground = 173.21 × tan(45) = 100·√3 m
The total height of the antenna from the ground is 100·√3 m
The correct option is therefore;
A. 100·√3 m
8. The coordinates of the point of intersection of the medians is given by the relation;
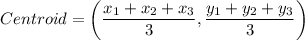
Where:
x₁, y₁ x₂, y₂, x₃, y₃ are the coordinates of the vertices
We therefore have;
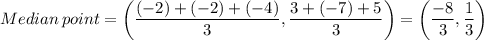
9. The perimeter of the rhombus = 4×√(First diagonal)/2)
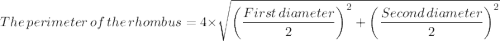
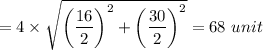
The correct option is A. 68 unit
10. The exterior angle of a regular polygon > 180°, therefore, the correct option is A. 150
 34
34 A. The exact value of sec(13π/6) = 2√3/3
B. The exact value of cot(7π/4) = -1
Step-by-step explanation:
* Lets study the four quadrants
# First quadrant the measure of all angles is between 0 and π/2
the measure of any angle is α
∴ All the angles are acute
∴ All the trigonometry functions of α are positive
# Second quadrant the measure of all angles is between π/2 and π
the measure of any angle is π - α
∴ All the angles are obtuse
∴ The value of sin(π - α) only is positive
sin(π - α) = sin(α) ⇒ csc(π - α) = cscα
cos(π - α) = -cos(α) ⇒ sec(π - α) = -sec(α)
tan(π - α) = -tan(α) ⇒ cot(π - α) = -cot(α)
# Third quadrant the measure of all angles is between π and 3π/2
the measure of any angle is π + α
∴ All the angles are reflex
∴ The value of tan(π + α) only is positive
sin(π + α) = -sin(α) ⇒ csc(π + α) = -cscα
cos(π + α) = -cos(α) ⇒ sec(π + α) = -sec(α)
tan(π + α) = tan(α) ⇒ cot(π + α) = cot(α)
# Fourth quadrant the measure of all angles is between 3π/2 and 2π
the measure of any angle is 2π - α
∴ All the angles are reflex
∴ The value of cos(2π - α) only is positive
sin(2π - α) = -sin(α) ⇒ csc(2π - α) = -cscα
cos(2π - α) = cos(α) ⇒ sec(2π - α) = sec(α)
tan(2π - α) = -tan(α) ⇒ cot(2π - α) = -cot(α)
* Now lets solve the problem
A. The measure of the angle 13π/6 = π/6 + 2π
- The means the terminal of the angle made a complete turn (2π) + π/6
∴ The angle of measure 13π/6 lies in the first quadrant
∴ sec(13π/6) = sec(π/6)
∵ sec(x) = 1/cos(x)
∵ cos(π/6) = √3/2
∴ sec(π/6) = 2/√3 ⇒ multiply up and down by √3
∴ sec(π/6) = 2/√3 × √3/√3 = 2√3/3
* The exact value of sec(13π/6) = 2√3/3
B. The measure of the angle 7π/4 = 2π - π/4
- The means the terminal of the angle lies in the fourth quadrant
∴ The angle of measure 7π/4 lies in the fourth quadrant
- In the fourth quadrant cos only is positive
∴ cot(2π - α) = -cot(α)
∴ cot(7π/4) = -cot(π/4)
∵ cot(x) = 1/tan(x)
∵ tan(π/4) = 1
∴ cot(π/4) = 1
∴ cot(7π/4) = -1
* The exact value of cot(7π/4) = -1
 34
34 A. The exact value of sec(13π/6) = 2√3/3
B. The exact value of cot(7π/4) = -1
Step-by-step explanation:
* Lets study the four quadrants
# First quadrant the measure of all angles is between 0 and π/2
the measure of any angle is α
∴ All the angles are acute
∴ All the trigonometry functions of α are positive
# Second quadrant the measure of all angles is between π/2 and π
the measure of any angle is π - α
∴ All the angles are obtuse
∴ The value of sin(π - α) only is positive
sin(π - α) = sin(α) ⇒ csc(π - α) = cscα
cos(π - α) = -cos(α) ⇒ sec(π - α) = -sec(α)
tan(π - α) = -tan(α) ⇒ cot(π - α) = -cot(α)
# Third quadrant the measure of all angles is between π and 3π/2
the measure of any angle is π + α
∴ All the angles are reflex
∴ The value of tan(π + α) only is positive
sin(π + α) = -sin(α) ⇒ csc(π + α) = -cscα
cos(π + α) = -cos(α) ⇒ sec(π + α) = -sec(α)
tan(π + α) = tan(α) ⇒ cot(π + α) = cot(α)
# Fourth quadrant the measure of all angles is between 3π/2 and 2π
the measure of any angle is 2π - α
∴ All the angles are reflex
∴ The value of cos(2π - α) only is positive
sin(2π - α) = -sin(α) ⇒ csc(2π - α) = -cscα
cos(2π - α) = cos(α) ⇒ sec(2π - α) = sec(α)
tan(2π - α) = -tan(α) ⇒ cot(2π - α) = -cot(α)
* Now lets solve the problem
A. The measure of the angle 13π/6 = π/6 + 2π
- The means the terminal of the angle made a complete turn (2π) + π/6
∴ The angle of measure 13π/6 lies in the first quadrant
∴ sec(13π/6) = sec(π/6)
∵ sec(x) = 1/cos(x)
∵ cos(π/6) = √3/2
∴ sec(π/6) = 2/√3 ⇒ multiply up and down by √3
∴ sec(π/6) = 2/√3 × √3/√3 = 2√3/3
* The exact value of sec(13π/6) = 2√3/3
B. The measure of the angle 7π/4 = 2π - π/4
- The means the terminal of the angle lies in the fourth quadrant
∴ The angle of measure 7π/4 lies in the fourth quadrant
- In the fourth quadrant cos only is positive
∴ cot(2π - α) = -cot(α)
∴ cot(7π/4) = -cot(π/4)
∵ cot(x) = 1/tan(x)
∵ tan(π/4) = 1
∴ cot(π/4) = 1
∴ cot(7π/4) = -1
* The exact value of cot(7π/4) = -1
F=ma
where F=force
m=mass
a=acceleration
Here,
F=4300
a=3.3m/s2
m=F/a
=4300/3.3
=1303.03kg

It will provide an instant answer!
