Step-by-step explanation:
Given is the function
xy =3
Use product rule to find derivative
xy'+y =0 OR 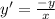
Arc length = 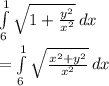
Substitute y = 3/x
WE get
arc length = 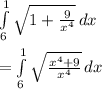
Using simpson rule for 1/3 we have
x(x^4+9)^1/2f(x)2 times or 4 times
13.162277663.162277663.16227766
1.53.751.6666666676.666666667
251.25
2.56.9327123121.109233974.43693588
39.4868329811.054092553
3.512.611998261.0295508784.118203512
416.27882061.0174262872.034852575
4.520.47101611.0109143754.0436575
525.179356621.0071742652.01434853
5.530.398396341.0049056644.019622656
636.124783741.0034662152.00693243
6.542.356374961.0025177514.010071002
749.091750831.0018724662.003744932
7.556.329943191.0014212124.005684849
864.070273921.001098032.00219606
8.572.312256911.0008616874.00344675
981.055536521.0006856362.001371272
9.590.299847731.0005523294.002209318
10100.04498991.0004498992.000899798
10.5110.29080881.0003701484.00148059
11121.03718441.0003073092.000614618
11.5132.28402211.0002572564.001029023
12144.03124661.000216994.82148E-05
52.270413638.711735605
Answer is 8.7117