(1) Square; triangle or pentagon
(2) Originally 146.6 m, now 139 m
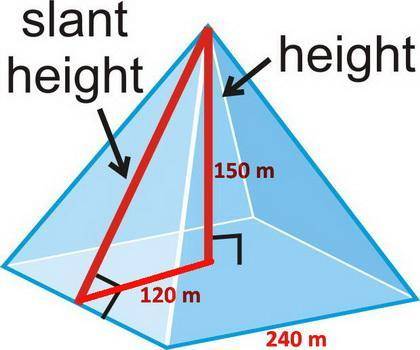
(3) (a) h = 150 m; (b) l = 240 m; (c) base = square;
(d) lateral area = 92 205 m²; (e) slope = 5/4
Step-by-step explanation:
(1) Base
The pyramids at Giza have square bases. Those are the most common, but the bases can have any number of shapes, e.g., triangles or pentagons.
(2) Size
The Great Pyramid was originally 146.6 m tall with a base that was 230.4 m on each side. It is now only 139 m tall, because the limestone casings have fallen away.
It would be possible to build a bigger pyramid today, because modern machinery can easily handle the massive stones.
(3) A larger pyramid
A larger modern pyramid might be 150 m tall and have a square base 240 m on each side.
(a) Height = 150 m
(b) Length = 240 m
(c) Base shape = square
(d) Surface Area
The square pyramid has four triangular faces.
(i) Side height
We can use Pythagoras' Theorem to calculate the side height s of the pyramid:
s² = 120² + 150² = 36 900 m²
s = √36900 = 192.1 m
(ii) Lateral area
The pyramid has four triangular faces.
Each triangle has a base of 240 m and a height of 192.1 m.
The formula for the area of a triangle is
A = ½bh
So. the area of the four triangles is
A = 4 × ½bh = 2bh = 2 × 240 m × 192.1 m = 92 205 m²
(e) Slope of pyramid
slope = Δy/Δx = 150/120 = 5/4