a) J = 13067 kg*m/s
b) J = 9240 kg*m/s
c) F = 2666.73 N
d) F = 21488.37 N
e) 135°
Explanation:
We know that the impulse could be calculated by:
J = ΔP
where ΔP is the change in the linear momentum:
Also:
P = MV
Where M is the mass and V is the velocity.
so:
where 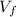 is the final velocity and
is the final velocity and 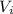 is the inicial velocity
is the inicial velocity
a)The impluse from turn is:
On the turn, 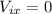 and
and 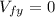 , the magnitude of the impulse on direction x and y are:
, the magnitude of the impulse on direction x and y are:
So, using pythagoras theorem the magnitude of the impulse is:
J = 13067 kg*m/s
b) The impluse from the collision is:
J = 0 - (1400)(6.6)
J = 9240 kg*m/s
c) Using the next equation:
FΔt = J
where F is the force, Δt is the time and J is the impulse.
Replacing J by the impulse due to the turn, Δt by 4.9s and solving for F we have that:
F = J / Δt
F = 13067 / 4.9 s
F = 2666.73 N
d) At the same way, replacing J by the impulse during the collision, Δt by 0.43s and solving for F we have that:
F = J / Δt
F = 9240 / 0.43
F = 21488.37 N
e) The force have the same direction than the impulse due to the turn, Then, if the impulse have a direction of -45°, the force have -45° or 135°