the cart's speed at point B is 15.72 ft/s
Explanation:
Given the data in the question;
The car travels from point A to C in 3.00 s, its average acceleration 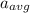 will be;
will be;
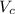 is 17.4 ft/s,
is 17.4 ft/s, 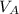 is 13.2 ft/s and Δt is 3.00 s
is 13.2 ft/s and Δt is 3.00 s
so we substitute
so average acceleration of the cart between the points A and B is 1.4 ft/s²
The instantaneous value of the velocity of the cart at point B will be;
now substitute [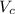 -
- 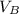 ] for Δv and t' for Δt
] for Δv and t' for Δt
so we substitute 17.4 ft/s for 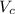 , 1.20 s for t' and
, 1.20 s for t' and 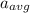 = 1.4 ft/s²
= 1.4 ft/s²
Therefore, the cart's speed at point B is 15.72 ft/s