10.5g of KBr
Explanation:
molarity = moles of solute / litres of solution
we are given the volume of the solution in milliliters but the formula uses litres so we have to convert
to convert to liters we divide the number of milliliters by 1000 ( because 1 liter has 1000 milliliters. )
so liters of solution = 92.7/1000 = 0.0927 L
we can now plug in what we are given and solve for moles of solute
recall molarity = moles of solute / litres of solution
molarity = 0.955M and liters of solution = 0.0927L
multiply both sides by 0.0927
we're left with moles of solute = 0.0885285 moles
Finally we must convert moles to grams
Molar mass of KBr = 39.0983 + 79.904 = g/mol
Using dimensional analysis we get 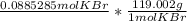
the mol KBr cancel out on both sides and we get 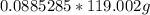 which is equal to 10.5g (rounded)
which is equal to 10.5g (rounded)
So we can conclude that 10.5g of KBr is dissolved in 92.7mL of a 0.955M solution.